
Flare researchers monitoring underground Telegram channels and cybercrime boards have noticed menace actors quickly sharing proof-of-concept exploits, offensive instruments, and stolen administrator credentials associated to not too long ago disclosed SmarterMail vulnerabilities, offering perception into how shortly attackers weaponize new safety flaws.
The exercise occurred inside days of the vulnerabilities being disclosed, with menace actors sharing and promoting exploit code and compromised entry tied to CVE-2026-24423 and CVE-2026-23760, crucial flaws that allow distant code execution and authentication bypass on uncovered electronic mail servers.
These vulnerabilities have since been confirmed in real-world assaults, together with ransomware campaigns, highlighting how attackers more and more goal electronic mail infrastructure as an preliminary entry level into company networks, permitting them to maneuver laterally and set up persistent footholds.
CVE-2026-24423 and CVE-2026-23760: Essential RCE and Auth Bypass Flaws
A number of not too long ago disclosed SmarterMail vulnerabilities created an ideal storm that made the platform extremely enticing to attackers. Amongst them, CVE-2026-24423 stands out as a crucial unauthenticated distant code execution flaw affecting variations previous to Construct 9511.
With a CVSS rating of 9.3 and no consumer interplay required, the flaw is especially suited to automation, large-scale scanning, and mass exploitation campaigns.
In parallel, extra vulnerabilities CVE-2026-23760 (CVSS 9.3) embrace authentication bypass and password reset logic flaws. It permits attackers to reset administrator credentials or achieve privileged entry to the platform. Analysis additionally exhibits that attackers have been shortly reverse-engineering patches to determine and weaponize these weaknesses inside days of launch.
When mixed, these points enabled full server takeover situations, the place attackers might transfer from application-level entry to working system management and probably domain-level compromise in linked environments.
From an attacker’s perspective, this mix is good: SmarterMail is a network-exposed service, typically holds a excessive belief place inside enterprise environments, and in lots of circumstances is monitored much less aggressively than endpoint programs protected by EDR.
As soon as proof-of-concept exploit code turns into obtainable, exploitation might be quickly operationalized – that means the timeline from vulnerability disclosure to ransomware deployment can shrink to days.
SmarterTools Breached by Personal Product Flaw, Ransomware Teams Observe
Current incidents exhibit precisely how this pipeline performs out.
In accordance with a SmarterTools report, SmarterTools was breached in January 2026 after attackers exploited an unpatched SmarterMail server operating on an inner VM that was uncovered inside their community.
The compromised setting included workplace and lab networks and a data-center phase linked by Energetic Listing, the place attackers moved laterally and impacted round a dozen Home windows servers.
The corporate shut down the affected infrastructure, restored programs from backup, rotated credentials, and eliminated some Home windows/AD dependencies. Having mentioned that, it was reported that core buyer companies and knowledge have been unaffected. Attackers gained an inner community foothold and tried typical ransomware-style post-exploitation actions; it wasn’t profitable, because of community segmentation.
In one other investigation printed by Bleeping Pc, ransomware operators gained preliminary entry by SmarterMail vulnerabilities and waited earlier than triggering encryption payloads, a traditional affiliate habits sample.
This sample is essential:
- Preliminary entry by way of electronic mail server vulnerability
- Credential harvesting or token extraction
- Lateral motion by way of Energetic Listing
- Persistence by way of scheduled duties or DFIR software abuse
- Ransomware deployment after staging interval
Some campaigns have been linked to the Warlock ransomware group, with overlaps noticed with nation-state-aligned exercise clusters.
Flare displays underground boards and Telegram channels the place menace actors share PoCs, exploits, and compromised credentials inside hours of disclosure.
Get early warning when your infrastructure is mentioned or focused by ransomware operators.
Electronic mail Servers: Id Infrastructure Attackers Goal First
Electronic mail servers sit at a novel intersection of belief and visibility.
They typically present:
- Area authentication tokens
- Password reset capabilities
- Exterior communication channels
- Entry to inner contact graphs
- Integration with id and listing companies
Attackers perceive that electronic mail ecosystems depend on multi-component authentication chains the place a single weak hyperlink can break total belief. Compromise the e-mail infrastructure and also you successfully compromise id.
1,200+ Weak Servers Recognized on Shodan
We discovered ~34,000 servers on Shodan with indications of operating SmarterMail. Out of the 34,000, there have been 17,754 distinctive servers.
An extra inspection of those servers exhibits that 1,185 are susceptible to authentication bypass or RCE flaws. Different publications discuss ~6,000 susceptible servers.
A geo-location evaluation of those 1,185 servers exhibits US dominance:
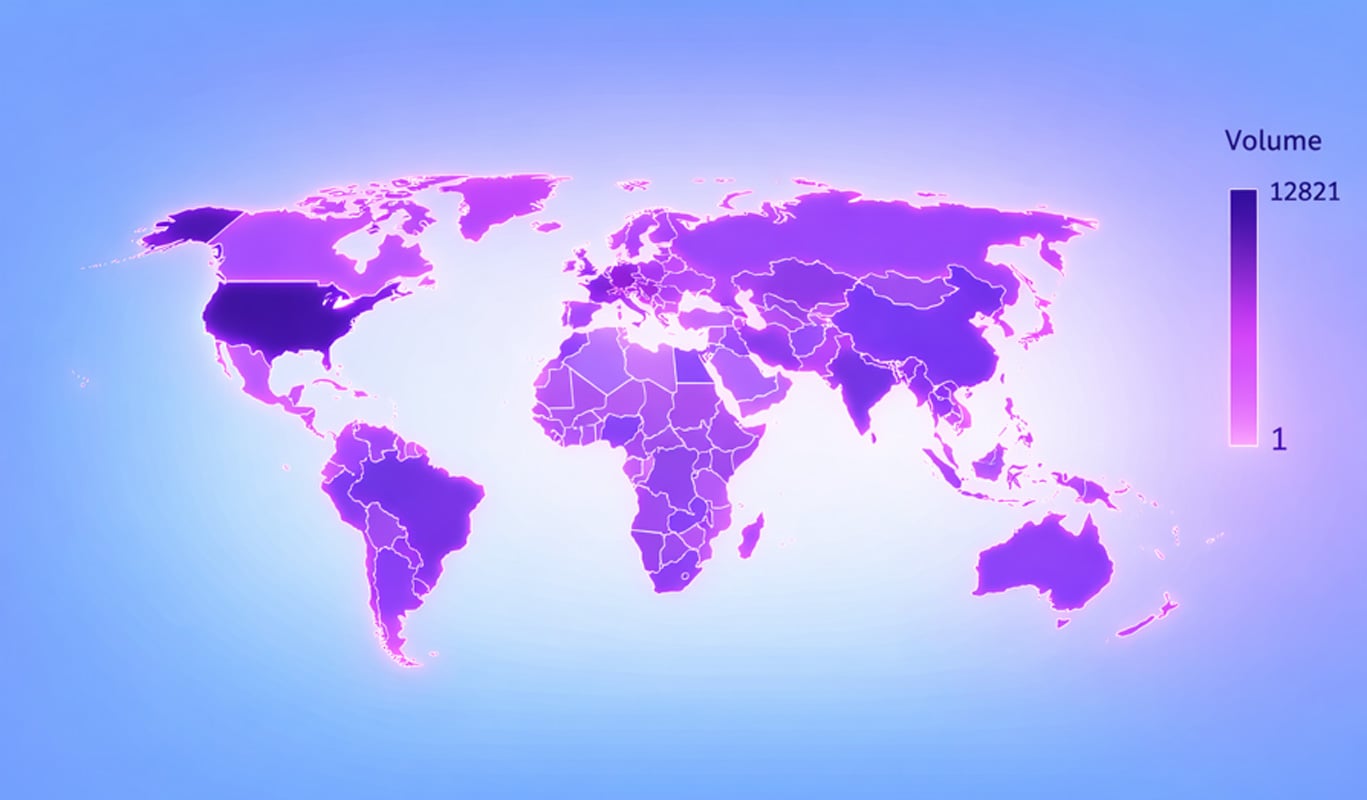
An extra evaluation of the ISPs and Organizations exhibits a really various distribution of open SmarterMail servers, many self-hosted admin panels, shared internet hosting, VPS suppliers, and general-purpose cloud networks, typical of deployment by people fairly than organizations.
This may increasingly point out that after the sturdy safety hype over the previous weeks, organizations have been fast to react and block this assault floor.
Underground Boards Share Exploits Inside Days of Disclosure
The underground ecosystems are quick to react to such publications. The CVEs have been printed across the starting of January, and on the identical day, there have been mentions and references to those vulnerabilities. Thus far, we’ve seen dozens of publications and references to those vulnerabilities.
That is regular underground habits in the case of crucial vulnerabilities.
Now we have additionally seen some extra malicious references. Just a few days after the primary publication, there have been references to Proof of Idea or exploit of the vulnerabilities. As an example, an Arabic-speaking Telegram channel exhibits PoC.
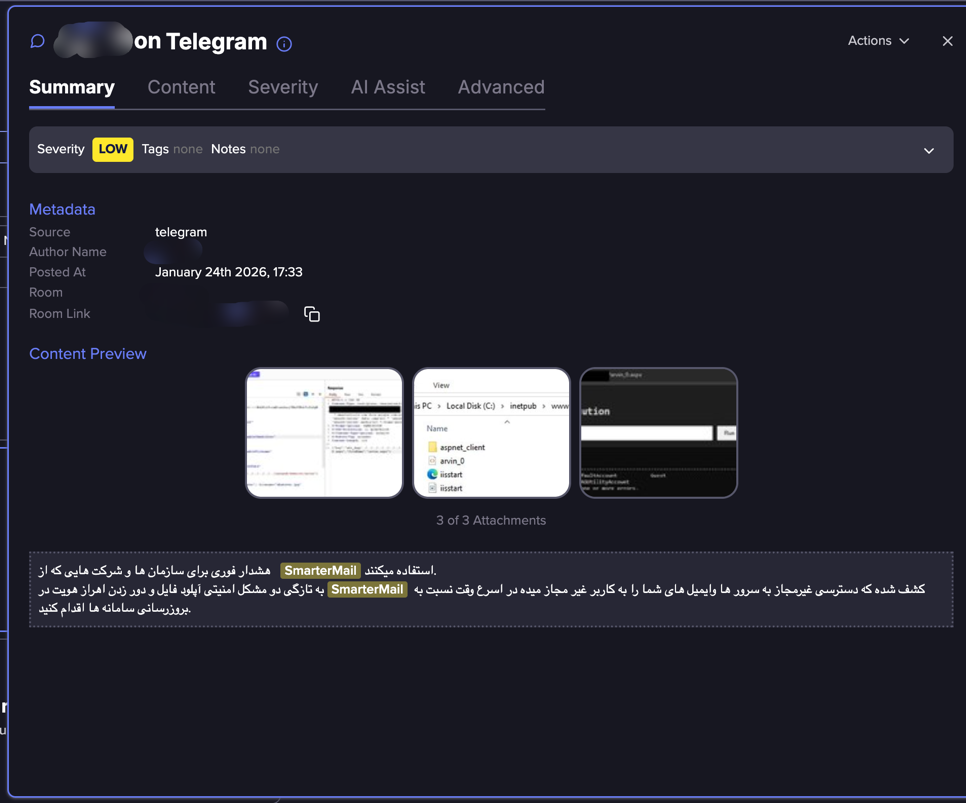
It’s also possible to see how the menace actor is displaying proof of idea:
And one other menace actor is displaying a proof of idea to this vulnerability:
In a Spanish-speaking Telegram group, we noticed references to an Offensive Safety Instrument:
On one other Telegram group, we noticed a knowledge dump of admin credentials highlighted because it comes from a compromised SmarterMail server:
When accessing one of many hyperlinks, you possibly can certainly see a protracted record of admin credentials and the domains (or login) to which they belong.
CISA Confirms Energetic Exploitation in Ransomware Campaigns
These vulnerabilities have been printed at first of 2026, CISA added CVE-2026-24423 to the Identified Exploited Vulnerabilities catalog at first of February 2026, after confirming energetic ransomware exploitation.
This confirms that attackers are fast to use newly found crucial RCE- associated vulnerabilities:
- Vulnerability disclosure
- PoC written and launched
- Mass scanning operation
- Weaponization: Knowledge exfiltration, Ransomware and so forth.
Timeline shrinking from months/weeks to days.
The way to Defend Electronic mail Infrastructure From Ransomware Entry
Many organizations nonetheless deal with electronic mail servers as “ONLY software infrastructure”. Effectively, they don’t seem to be!
They’re id infrastructures that allow many follow-up assault vectors, in addition to containing secrets and techniques and enterprise logic. Defensive priorities ought to embrace:
- Patch Urgency: Essential electronic mail server vulnerabilities ought to be handled like area controller vulnerabilities.
- Id Telemetry: Organizations ought to monitor these environments for:
- Admin password resets
- API calls to exterior hosts
- Surprising outbound HTTP from mail servers
- Community Segmentation: Electronic mail infrastructure ought to by no means have unrestricted entry to inner networks.
- Menace Searching Observe:
- API abuse patterns
- Scheduled process persistence
- Surprising tooling like DFIR frameworks or distant admin instruments
Electronic mail Servers Are Id Infrastructure—Safe Them Accordingly
The SmarterMail circumstances present as soon as once more how trendy cybercrime operations are fast so as to add newly found preliminary entry to their ongoing operation.
It additionally re-emphasizes the crucial function electronic mail servers take within the trendy group:
- Id brokers
- Belief anchors
- Enterprise logic
- Invaluable reconnaissance knowledge for follow-up cybercrime
Organizations that proceed treating them as simply “messaging programs” will stay susceptible to this new technology of intrusion pipelines.
Be taught extra by signing up for our free trial.
Sponsored and written by Flare.


