A big provide chain assault hit NPM after 16 standard Gluestack ‘react-native-aria’ packages with over 950,000 weekly downloads had been compromised to incorporate malicious code that acts as a distant entry trojan (RAT).
BleepingComputer decided that the compromise started on June 6 at 4:33 PM EST, when a brand new model of the react-native-aria/focus bundle was revealed to NPM. Since then, 16 of the 20 Gluestack react-native-aria packages have been compromised on NPM, with the menace actors publishing a brand new model as just lately as two hours in the past.
Supply: BleepingComputer
The availability chain assault was found by cybersecurity agency Aikido Safety, who found obfuscated code injected into the lib/index.js file for the next packages:
| Bundle Identify | Model | Weekly Downloads |
| react-native-aria/button | 0.2.11 | 51,000 |
| react-native-aria/checkbox | 0.2.11 | 81,000 |
| react-native-aria/combobox | 0.2.10 | 51,000 |
| react-native-aria/disclosure | 0.2.9 | 3 |
| react-native-aria/focus | 0.2.10 | 100,000 |
| react-native-aria/interactions | 0.2.17 | 125,000 |
| react-native-aria/listbox | 0.2.10 | 51,000 |
| react-native-aria/menu | 0.2.16 | 22,000 |
| react-native-aria/overlays | 0.3.16 | 96,000 |
| react-native-aria/radio | 0.2.14 | 78,000 |
| react-native-aria/change | 0.2.5 | 477 |
| react-native-aria/toggle | 0.2.12 | 81,000 |
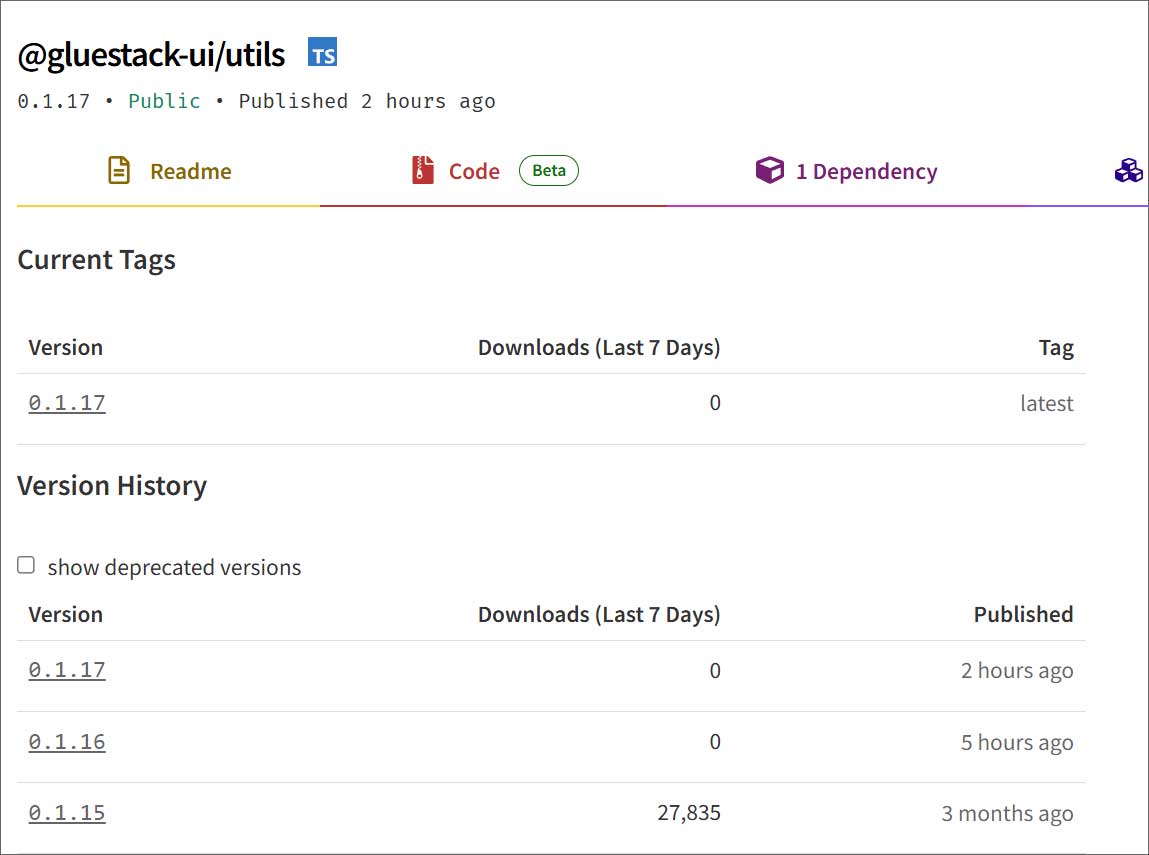
| react-native-aria/utils | 0.2.13 | 120,000 |
| gluestack-ui/utils | 0.1.17 | 55,000 |
| react-native-aria/separator | 0.2.7 | 65 |
| react-native-aria/slider | 0.2.13 | 51,000 |
These packages are very talked-about, with roughly 960,000 weekly downloads, making this a provide chain assault that might have widespread penalties.
The malicious code is closely obfuscated and is appended to the final line of supply code within the file, padded with many areas, so it is not simply noticed when utilizing the code viewer on the NPM web site.
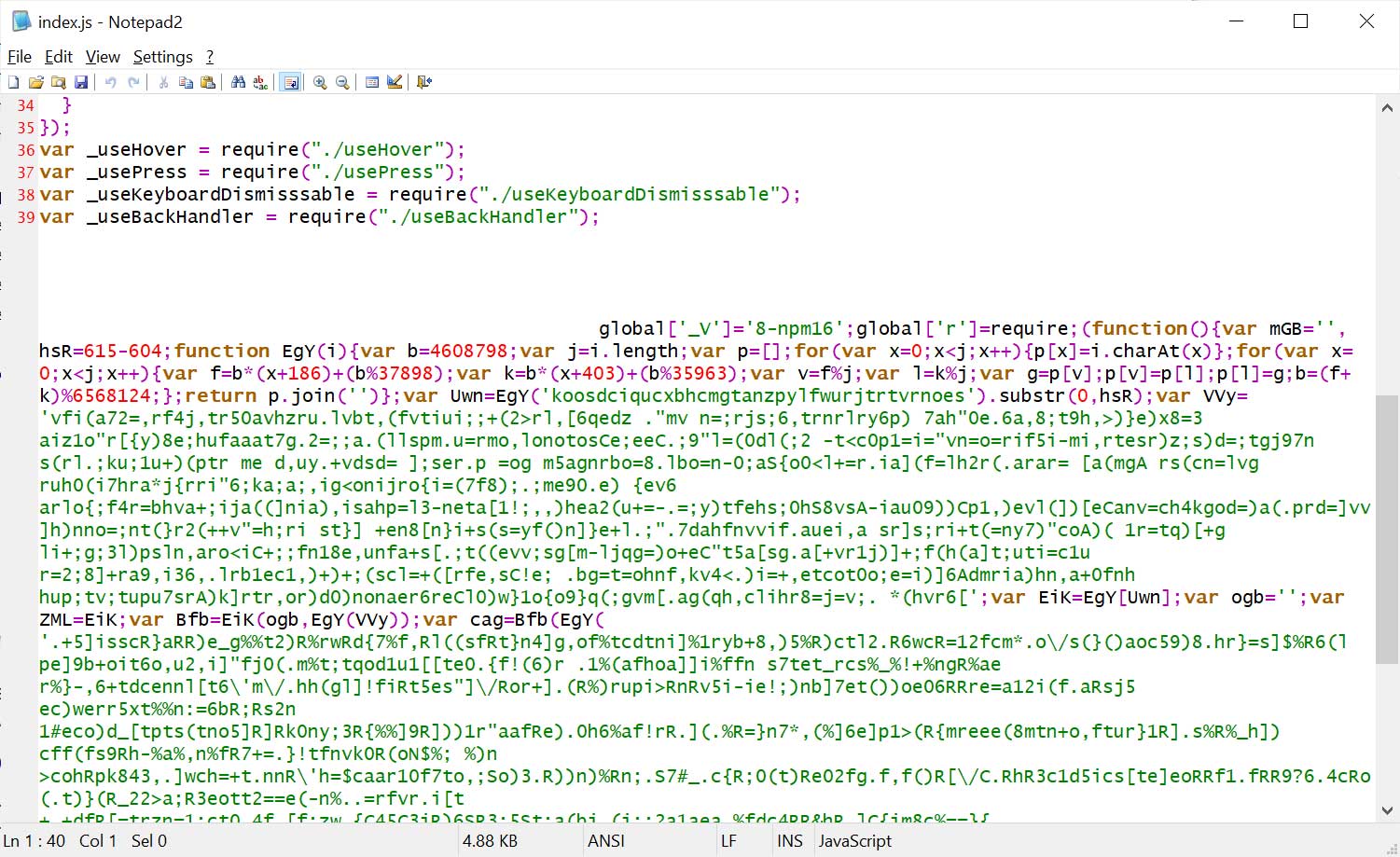
Supply: BleepingComputer
Aikido advised BleepingComputer that the malicious code is sort of an identical to a distant entry trojan in one other NPM compromise they found final month.
The researcher’s evaluation of the earlier marketing campaign explains that the distant entry trojan will hook up with the attackers’ command and management server and obtain instructions to execute.
These instructions embody:
- cd – Change present working listing
- ss_dir – Reset listing to script’s path
- ss_fcd:<path> – Drive change listing to <path>
- ss_upf:f,d – Add single file f to vacation spot d
- ss_upd:d,dest – Add all recordsdata underneath listing d to vacation spot dest
- ss_stop – Units a cease flag to interrupt present add course of
- Every other enter – Handled as a shell command, executed by way of child_process.exec()
The trojan additionally performs Home windows PATH hijacking by prepending a faux Python path (%LOCALAPPDATApercentProgramsPythonPython3127) to the PATH setting variable, permitting the malware to silently override reliable python or pip instructions to execute malicious binaries.
Aikido sercurity researcher Charlie Eriksen has tried to contact Gluestack concerning the compromise by creating GitHub points on every of the undertaking’s repositories, however there has not been any response at the moment.
“No response from bundle maintainers (it is morning on a saturday within the US which is prob precisely why its taking place now),” Arkido advised BleepingComputer.
“NPM we’ve got contacted and reported every bundle, this can be a course of that often takes a number of days for NPM to handle although.”
Aikido additionally attributes this assault to the identical menace actors who compromised 4 different NPM packages earlier this week named biatec-avm-gas-station, cputil-node, lfwfinance/sdk, and lfwfinance/sdk-dev.
BleepingComputer reached out to Gluestack concerning the compromised packages however has not obtained a reply at the moment.


