Greater than 46,000 internet-facing Grafana situations stay unpatched and uncovered to a client-side open redirect vulnerability that permits executing a malicious plugin and account takeover.
The flaw is tracked as CVE-2025-4123 and impacts a number of variations of the open-source platform used for monitoring and visualizing infrastructure and utility metrics.
The vulnerability was found by bug bounty hunter Alvaro Balada and was addressed in safety updates that Grafana Labs launched on Could 21.
Nevertheless, as of scripting this, greater than a 3rd of all Grafana situations reachable over the general public web haven’t been patched, in response to researchers at aplication safety firm OX Safety, who consult with the bug as ‘The Grafana Ghost’.
The analysts instructed BleepingComputer that their work centered on demonstrating the flexibility to weaponize Balada’s discovering.
After figuring out variations weak to the assault, they assesed the publicity by correlating the info with the platform’s distribution throughout the ecosystem.
They discovered 128,864 situations uncovered on-line, with 46,506 nonetheless operating weak variations that may nonetheless be exploited. This corresponds to a share of about 36%.
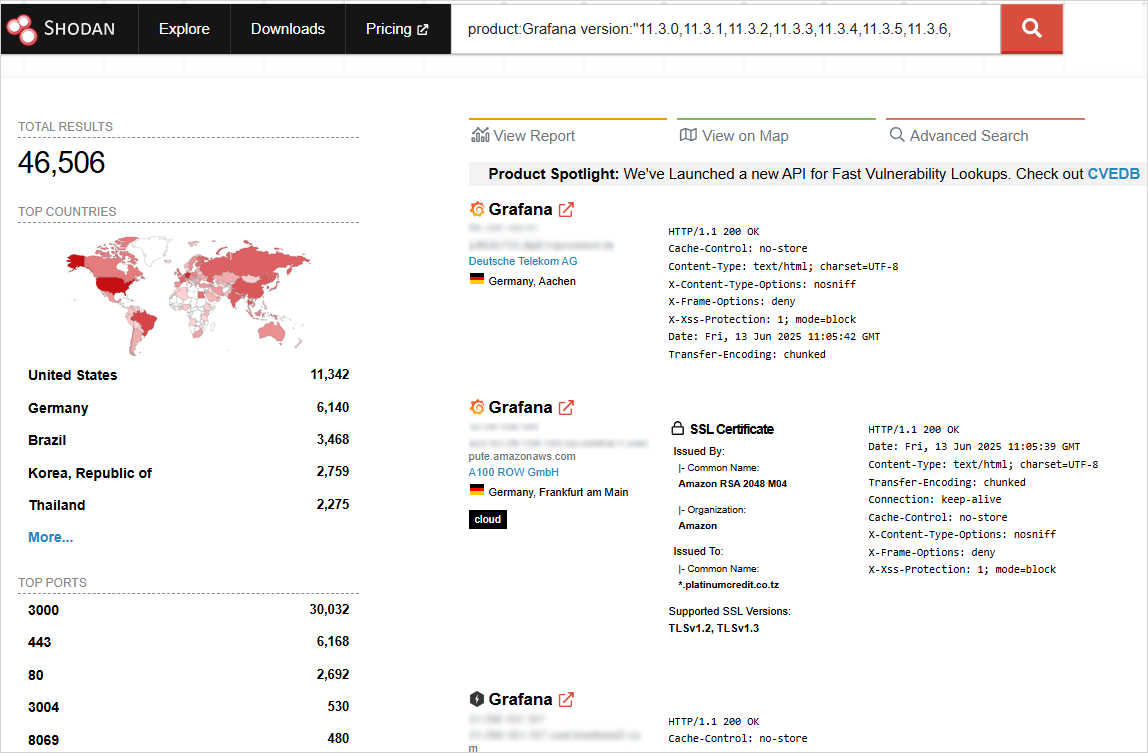
Supply: BleepingComputer
OX Safety’s in-depth evaluation of CVE-2025-4123 uncovered that, by means of a collection of exploitation steps combining client-side path traversal with open redirect mechanics, attackers can lure victims into clicking URLs that result in loading a malicious Grafana plugin from a web site managed by the risk actor.
The malicious hyperlinks may very well be used to execute arbitrary JavaScript within the person’s browser, the researchers say.
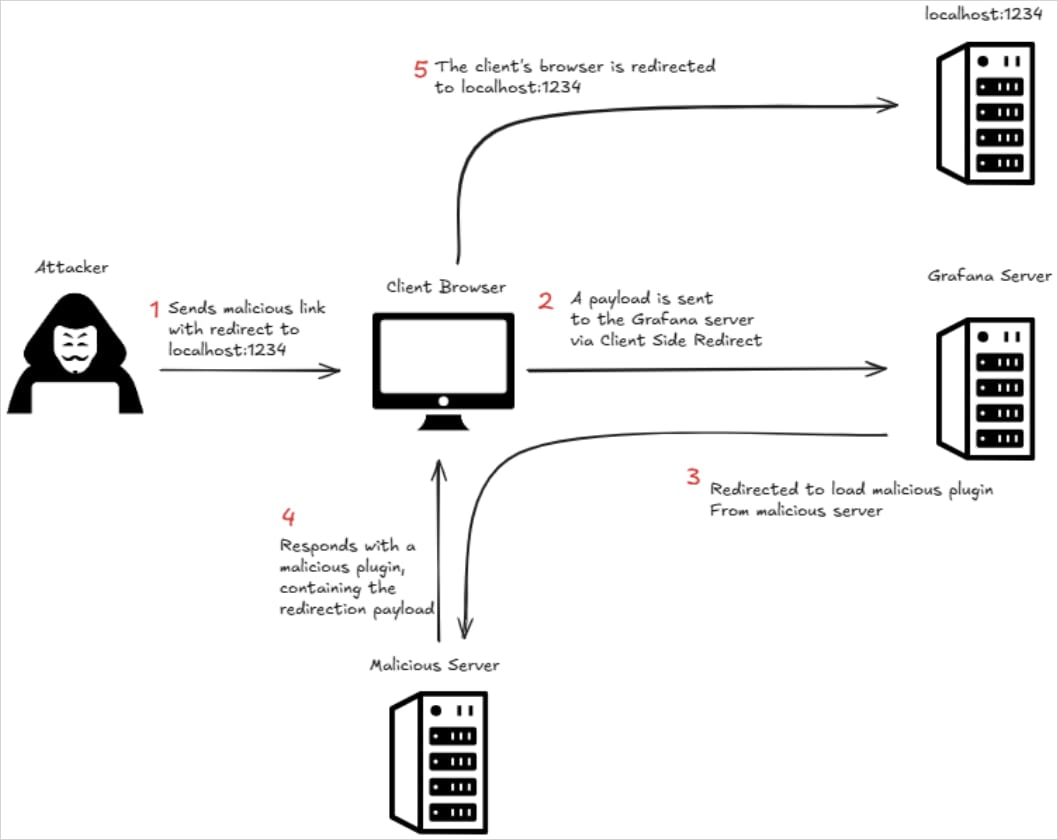
Supply: OX Safety
The exploit doesn’t require elevated privileges and may operate even when nameless entry is enabled.
The flaw permits attackers to hijack person periods, change account credentials, and, in circumstances the place the Grafana Picture Renderer plugin is put in, carry out server-side request forgery (SSRF) to learn inner sources.
Whereas the default Content material Safety Coverage (CSP) in Grafana gives some safety, it doesn’t stop exploitation because of limitations in client-side enforcement.
OX Safety’s exploit demonstrates that CVE-2025-4123 will be exploited client-side and may very well be leveraged to bypass fashionable browser normalization mechanisms by by means of JavaScript routing logic native to Grafana.
This permits attackers to use URL dealing with inconsistencies to serve malicious plugins, which in flip modify person e mail addresses, making account hijacking by way of password resets trivial.
Though CVE-2025-4123 has a number of exploitation necessities, like person interplay, an lively person session when the sufferer clicks the hyperlink, and having the plugin function enabled (is enabled by default), the massive variety of uncovered situations and the shortage for want of authentication create a major assault floor.
To mitigate the danger of exploitation, it’s endorsed that Grafana directors improve to variations 10.4.18+security-01, 11.2.9+security-01, 11.3.6+security-01, 11.4.4+security-01, 11.5.4+security-01, 11.6.1+security-01, and 12.0.0+security-01.
Patching used to imply complicated scripts, lengthy hours, and infinite hearth drills. Not anymore.
On this new information, Tines breaks down how fashionable IT orgs are leveling up with automation. Patch quicker, cut back overhead, and concentrate on strategic work — no complicated scripts required.



