
Malware analyst found a brand new model of the Atomic macOS info-stealer (often known as ‘AMOS’) that comes with a backdoor, to attackers persistent entry to compromised techniques.
The brand new element permits executing arbitrary distant instructions, it survives reboots, and permits sustaining management over contaminated hosts indefinitely.
MacPaw’s cybersecurity division Moonlock analyzed the backdoor in Atomic malware after a tip from impartial researcher g0njxa, a detailed observer of infostealer exercise.
“AMOS malware campaigns have already reached over 120 international locations, with the USA, France, Italy, the UK, and Canada among the many most affected,” the researchers say.
“The backdoored model of Atomic macOS Stealer now has the potential to achieve full entry to hundreds of Mac gadgets worldwide.”
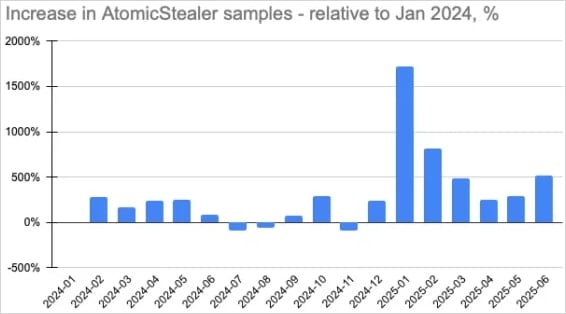
Supply: Moonlock
Evolution of the Atomic stealer
The Atomic stealer, first documented in April 2023, is a malware-as-a-service (MaaS) operation promoted on Telegram channels for a hefty subscription of $1,000 monthly. It targets macOS recordsdata, cryptocurrency extensions, and consumer passwords saved on internet browsers.
In November 2023, it supported the first-ever enlargement of ‘ClearFake’ campaigns onto macOS, whereas in September 2024, it was noticed in a large-scale marketing campaign by the cybercrime group’ Marko Polo,’ who deployed it on Apple computer systems.
Moonlock stories that Atomic has just lately shifted from broad distribution channels like cracked software program websites, to focused phishing aimed toward cryptocurrency house owners, in addition to job interview invites to freelancers.
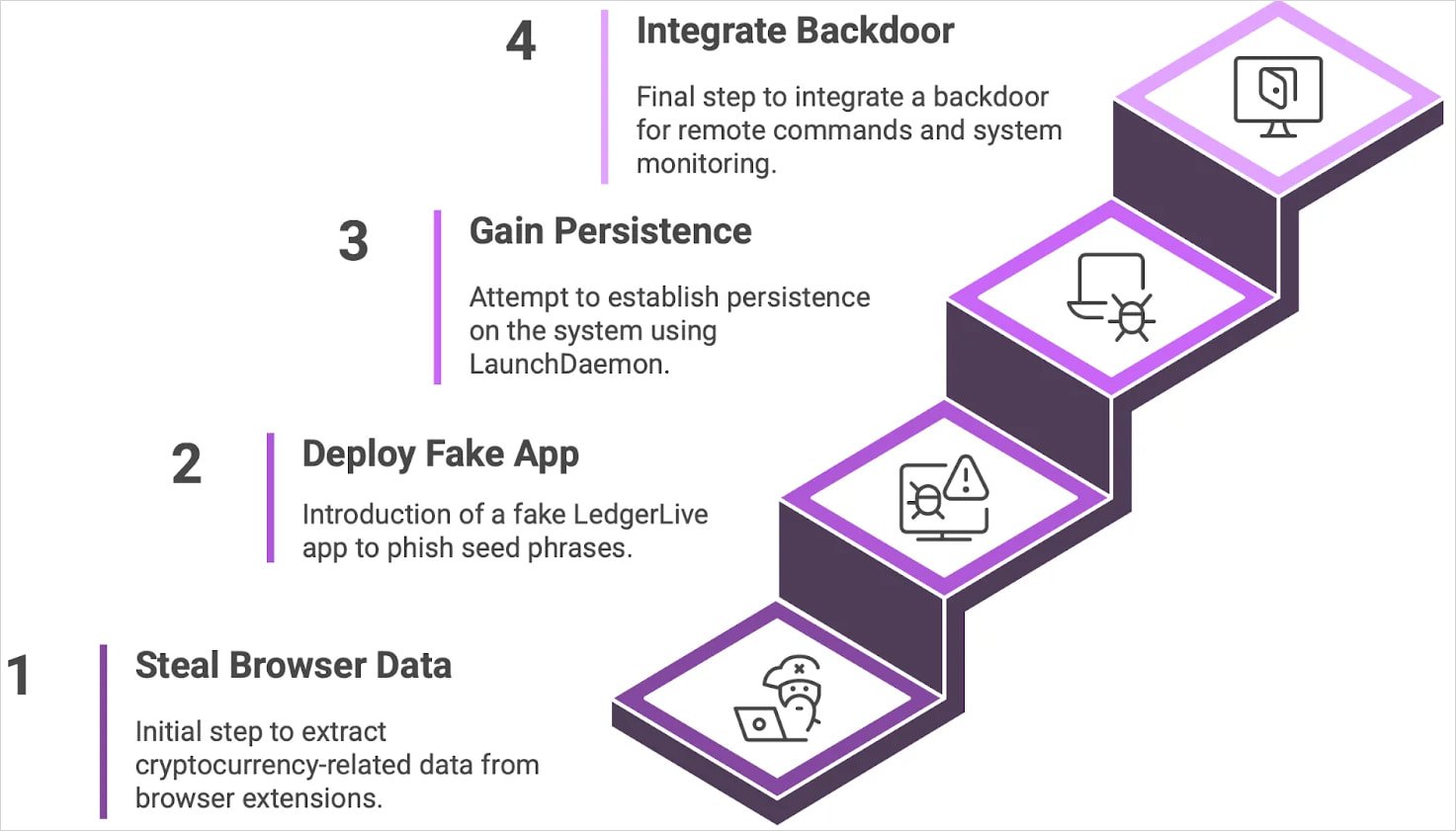
The analyzed model of the malware comes with an embedded backdoor, makes use of of LaunchDaemons to outlive reboots on macOS, ID-based sufferer monitoring, and new command-and-control infrastructure.
Supply: Moonlock
A backdoor into your Mac
The core backdoor executable is a binary named ‘.helper,’ downloaded and saved within the sufferer’s residence listing as a hidden file post-infection, the researchers say.
A persistent wrapper script named ‘.agent’ (additionally hidden) runs ‘.helper’ in a loop because the logged-in consumer, whereas a LaunchDaemon (com.finder.helper) put in by way of AppleScript ensures that ‘.agent’ executes at system startup.
This motion is carried out with elevated privileges utilizing the consumer’s password stolen throughout the preliminary an infection part underneath a false pretext. The malware can then execute instructions and alter possession of the LaunchDaemon PLIST to ‘root:wheel’ (superuser stage on macOS).

Supply: Moonlock
The backdoor permits the risk actors to execute instructions remotely, log key strokes, introduce further payloads, or discover lateral motion potential.
To evade detection, the backdoor checks for sandbox or digital machine environments utilizing ‘system_profiler’ and likewise options string obfuscation.
The evolution of Atomic malware exhibits that macOS customers have gotten extra engaging targets and malicious campaigns aimed toward them are more and more refined.


