CISA has confirmed {that a} most severity vulnerability in AMI’s MegaRAC Baseboard Administration Controller (BMC) software program is now actively exploited in assaults.
The MegaRAC BMC firmware gives distant system administration capabilities for troubleshooting servers with out being bodily current, and it is utilized by a number of distributors (together with HPE, Asus, and ASRock) that provide tools to cloud service suppliers and information facilities.
This authentication bypass safety flaw (tracked as CVE-2024-54085) will be exploited by distant unauthenticated attackers in low-complexity assaults that do not require consumer interplay to hijack and doubtlessly brick unpatched servers.
“Exploitation of this vulnerability permits an attacker to remotely management the compromised server, remotely deploy malware, ransomware, firmware tampering, bricking motherboard elements (BMC or doubtlessly BIOS/UEFI), potential server bodily harm (over-voltage / bricking), and indefinite reboot loops {that a} sufferer can not cease,” defined provide chain safety firm Eclypsium who found the vulnerability.
Eclypsium researchers found CVE-2024-54085 whereas analyzing patches issued by AMI for one more authentication bypass bug (CVE-2023-34329) disclosed in July 2023.
In March, when the AMI launched safety updates to repair CVE-2024-54085, Eclypsium discovered greater than 1,000 servers on-line that have been doubtlessly uncovered to assaults and mentioned that creating an exploit is “not difficult,” seeing that MegaRAC BMC firmware binaries aren’t encrypted.
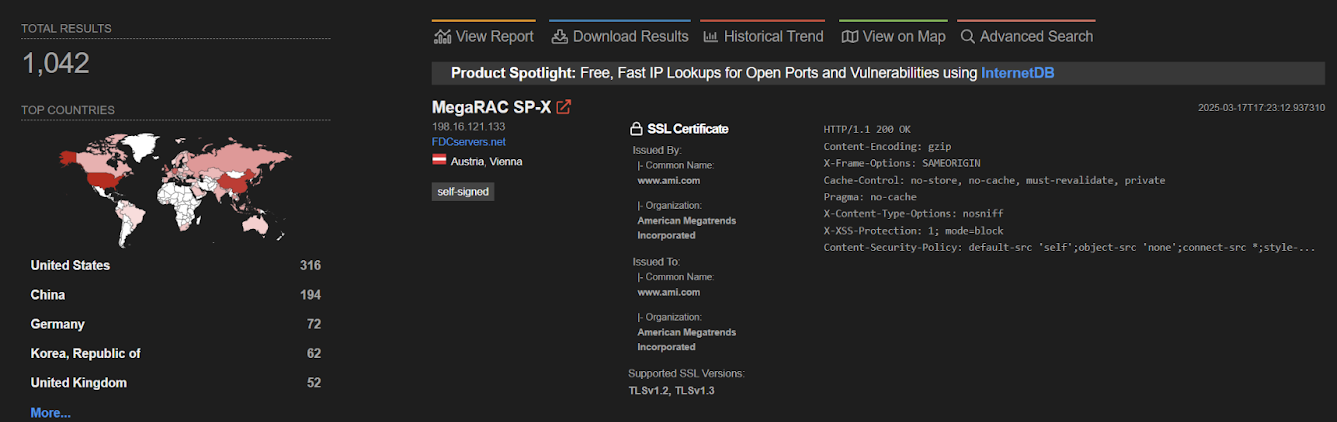
”To our information, the vulnerability solely impacts AMI’s BMC software program stack. Nevertheless, since AMI is on the high of the BIOS provide chain, the downstream influence impacts over a dozen producers,” Eclypsium added.
CISA confirmed on Wednesday that thevulnerability is now exploited within the wild and added it to the Recognized Exploited Vulnerabilities catalog, which lists safety flaws flagged by the cybersecurity company as actively exploited in assaults.
As mandated by the November 2021 Binding Operational Directive (BOD) 22-01, Federal Civilian Govt Department (FCEB) companies now have three weeks, till July sixteenth, to patch their servers in opposition to these ongoing assaults.
Though BOD 22-01 solely applies to federal companies, all community defenders are suggested to prioritize patching this vulnerability as quickly as attainable to dam potential breaches.
“These kinds of vulnerabilities are frequent assault vectors for malicious cyber actors and pose important dangers to the federal enterprise,” CISA warned.
Patching used to imply complicated scripts, lengthy hours, and infinite fireplace drills. Not anymore.
On this new information, Tines breaks down how fashionable IT orgs are leveling up with automation. Patch quicker, scale back overhead, and deal with strategic work — no complicated scripts required.



