No less than 18 in style JavaScript code packages which are collectively downloaded greater than two billion occasions every week have been briefly compromised with malicious software program as we speak, after a developer concerned in sustaining the initiatives was phished. The assault seems to have been rapidly contained and was narrowly targeted on stealing cryptocurrency. However consultants warn {that a} comparable assault with a barely extra nefarious payload may rapidly result in a disruptive malware outbreak that’s far tougher to detect and restrain.
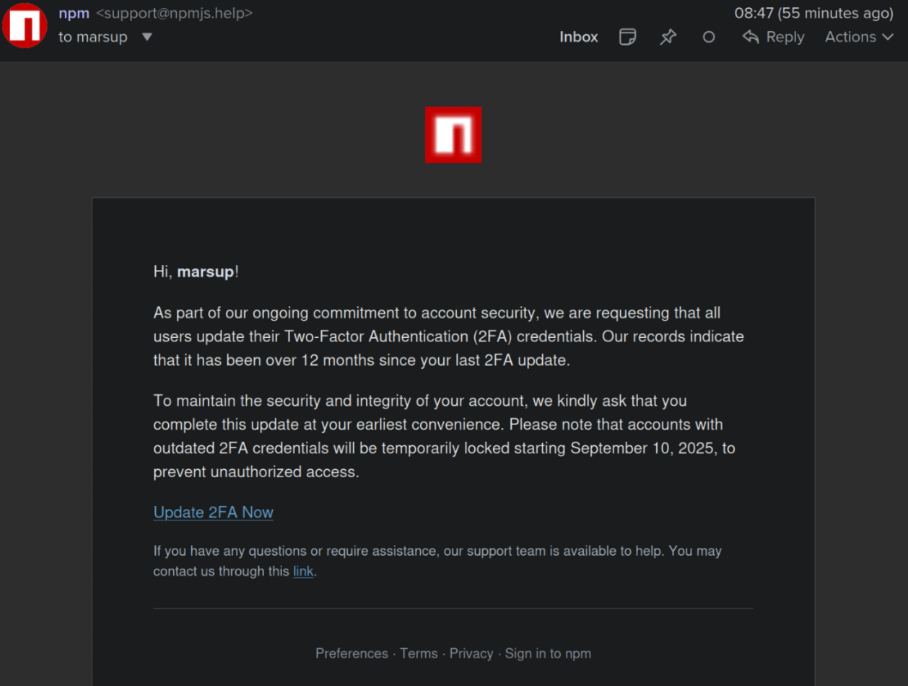
This phishing e-mail lured a developer into logging in at a faux NPM web site and supplying a one-time token for two-factor authentication. The phishers then used that developer’s NPM account so as to add malicious code to at the least 18 in style JavaScript code packages.
Akido is a safety agency in Belgium that displays new code updates to main open-source code repositories, scanning any code updates for suspicious and malicious code. In a weblog submit revealed as we speak, Akido stated its techniques discovered malicious code had been added to at the least 18 widely-used code libraries accessible on NPM (quick for) “Node Package deal Supervisor,” which acts as a central hub for JavaScript improvement and the most recent updates to widely-used JavaScript parts.
JavaScript is a robust web-based scripting language utilized by numerous web sites to construct a extra interactive expertise with customers, similar to getting into knowledge right into a type. However there’s no want for every web site developer to construct a program from scratch for getting into knowledge right into a type after they can simply reuse already current packages of code at NPM which are particularly designed for that objective.
Sadly, if cybercriminals handle to phish NPM credentials from builders, they will introduce malicious code that enables attackers to essentially management what folks see of their internet browser after they go to an internet site that makes use of one of many affected code libraries.
In keeping with Akido, the attackers injected a chunk of code that silently intercepts cryptocurrency exercise within the browser, “manipulates pockets interactions, and rewrites fee locations in order that funds and approvals are redirected to attacker-controlled accounts with none apparent indicators to the consumer.”
“This malware is basically a browser-based interceptor that hijacks each community visitors and software APIs,” Akido researcher Charlie Eriksen wrote. “What makes it harmful is that it operates at a number of layers: Altering content material proven on web sites, tampering with API calls, and manipulating what customers’ apps imagine they’re signing. Even when the interface appears appropriate, the underlying transaction will be redirected within the background.”
Akido stated it used the social community Bsky to inform the affected developer, Josh Junon, who rapidly replied that he was conscious of getting simply been phished. The phishing e-mail that Junon fell for was half of a bigger marketing campaign that spoofed NPM and informed recipients they have been required to replace their two-factor authentication (2FA) credentials. The phishing website mimicked NPM’s login web page, and intercepted Junon’s credentials and 2FA token. As soon as logged in, the phishers then modified the e-mail tackle on file for Junon’s NPM account, quickly locking him out.
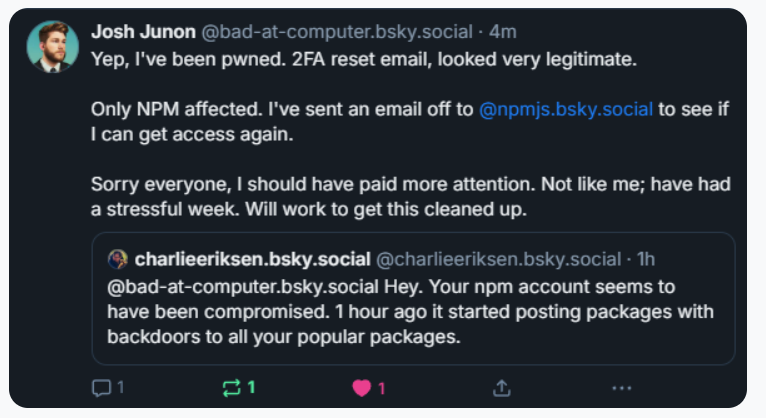
Aikido notified the maintainer on Bluesky, who replied at 15:15 UTC that he was conscious of being compromised, and beginning to clear up the compromised packages.
Junon additionally issued a mea culpa on HackerNews, telling the neighborhood’s coder-heavy readership, “Hello, yep I received pwned.”
“It appears and feels a bit like a focused assault,” Junon wrote. “Sorry everybody, very embarrassing.”
Philippe Caturegli, “chief hacking officer” on the safety consultancy Seralys, noticed that the attackers seem to have registered their spoofed web site — npmjs[.]assist — simply two days earlier than sending the phishing e-mail. The spoofed web site used providers from dnsexit[.]com, a “dynamic DNS” firm that additionally presents “100% free” domains that may immediately be pointed at any IP tackle managed by the consumer.
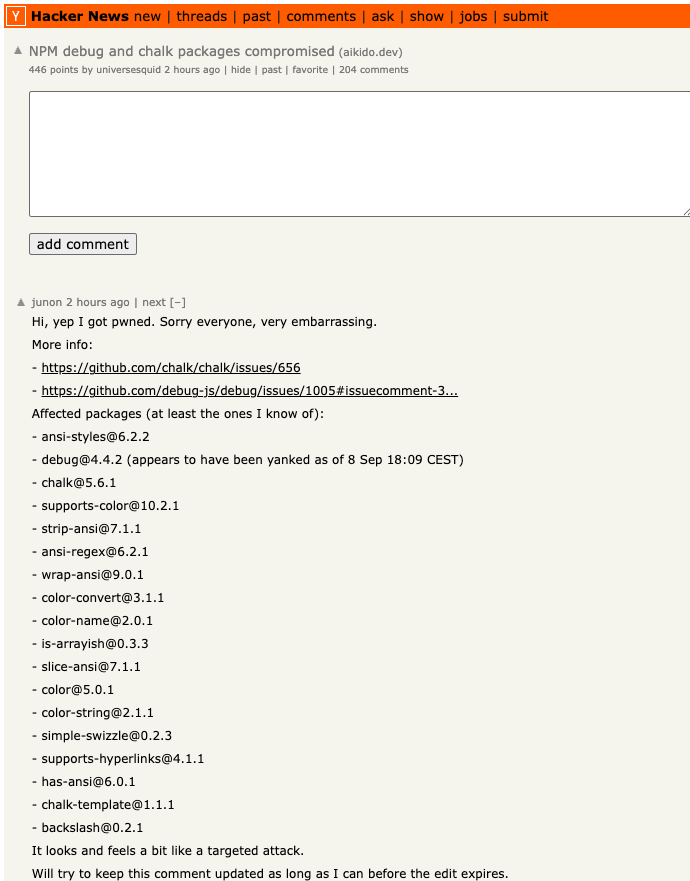
Junon’s mea cupla on Hackernews as we speak listed the affected packages.
Caturegli stated it’s outstanding that the attackers on this case weren’t extra bold or malicious with their code modifications.
“The loopy half is that they compromised billions of internet sites and apps simply to focus on a few cryptocurrency issues,” he stated. “This was a provide chain assault, and it may simply have been one thing a lot worse than crypto harvesting.”
Akito’s Eriksen agreed, saying numerous web sites dodged a bullet as a result of this incident was dealt with in a matter of hours. For instance of how these supply-chain assaults can escalate rapidly, Eriksen pointed to one other compromise of an NPM developer in late August that added malware to “nx,” an open-source code improvement toolkit with as many as six million weekly downloads.
Within the nx compromise, the attackers launched code that scoured the consumer’s gadget for authentication tokens from programmer locations like GitHub and NPM, in addition to SSH and API keys. However as a substitute of sending these stolen credentials to a central server managed by the attackers, the malicious code created a brand new public repository within the sufferer’s GitHub account, and revealed the stolen knowledge there for all of the world to see and obtain.
Eriksen stated coding platforms like GitHub and NPM ought to be doing extra to make sure that any new code commits for broadly-used packages require a better degree of attestation that confirms the code in query was in actual fact submitted by the one who owns the account, and never simply by that particular person’s account.
“Extra in style packages ought to require attestation that it got here by means of trusted provenance and never simply randomly from some location on the Web,” Eriksen stated. “The place does the bundle get uploaded from, by GitHub in response to a brand new pull request into the principle department, or elsewhere? On this case, they didn’t compromise the goal’s GitHub account. They didn’t contact that. They only uploaded a modified model that didn’t come the place it’s anticipated to come back from.”
Eriksen stated code repository compromises will be devastating for builders, lots of whom find yourself abandoning their initiatives totally after such an incident.
“It’s unlucky as a result of one factor we’ve seen is folks have their initiatives get compromised they usually say, ‘You recognize what, I don’t have the vitality for this and I’m simply going to deprecate the entire bundle,’” Eriksen stated.
Kevin Beaumont, a ceaselessly quoted safety skilled who writes about safety incidents on the weblog doublepulsar.com, has been following this story carefully as we speak in frequent updates to his account on Mastodon. Beaumont stated the incident is a reminder that a lot of the planet nonetheless is determined by code that’s finally maintained by an exceedingly small variety of people who find themselves largely overburdened and under-resourced.
“For concerning the previous 15 years each enterprise has been growing apps by pulling in 178 interconnected libraries written by 24 folks in a shed in Skegness,” Beaumont wrote on Mastodon. “For concerning the previous 2 years orgs have been shopping for AI vibe coding instruments, the place some exec screams ‘make on-line store’ into a pc and 389 libraries are added and an app is farted out. The output = if you wish to personal the world’s firms, simply phish one man in Skegness.”
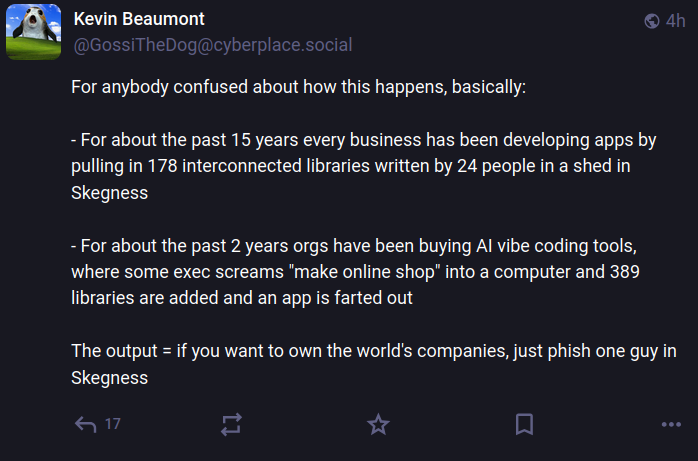
Picture: https://infosec.change/@GossiTheDog@cyberplace.social.
Akido lately launched a product that goals to assist improvement groups make sure that each code library used is checked for malware earlier than it may be used or put in. Nicholas Weaver, a researcher with the Worldwide Pc Science Institute, a nonprofit in Berkeley, Calif., stated Akido’s new providing exists as a result of many organizations are nonetheless one profitable phishing assault away from a supply-chain nightmare.
Weaver stated a majority of these supply-chain compromises will proceed so long as folks accountable for sustaining widely-used code proceed to depend on phishable types of 2FA.
“NPM ought to solely help phish-proof authentication,” Weaver stated, referring to bodily safety keys which are phish-proof — which means that even when phishers handle to steal your username and password, they nonetheless can’t log in to your account with out additionally possessing that bodily key.
“All crucial infrastructure wants to make use of phish-proof 2FA, and given the dependencies in fashionable software program, archives similar to NPM are completely crucial infrastructure,” Weaver stated. “That NPM doesn’t require that every one contributor accounts use safety keys or comparable 2FA strategies ought to be thought of negligence.”

