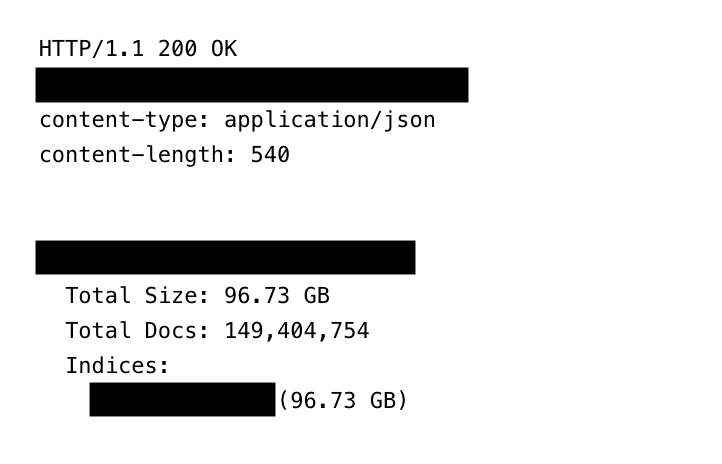
Jeremiah Fowler, a veteran safety researcher, lately stumbled upon 149,404,754 distinctive logins and passwords, totaling about 96GB of uncooked information.
There was no encryption… and it didn’t actually have a password.
Sharing his findings with ExpressVPN, Fowler famous, “The publicly uncovered database was not password-protected or encrypted.” The gathering was so giant and detailed that it wasn’t only a checklist of names; it included emails, usernames, passwords, and the particular web site hyperlinks wanted to log into the accounts.
The scale of this publicity covers virtually each nook of the web. Whereas shopper accounts like Gmail and Fb make up the most important chunk, the database additionally contained delicate logins for cryptocurrency exchanges and even relationship websites.
| Platform | Estimated Compromised Accounts |
|---|---|
| 48 Million | |
| 17 Million | |
| 6.5 Million | |
| 4 Million | |
| 3.4 Million | |
| 1.5 Million | |
| 1.4 million | |
| 900,000 | |
| 780,000 | |
| 420,000 | |
| 100,000 |

Maybe most alarmingly, the cache additionally contained credentials linked to .gov domains from a number of nations.
Whereas not each authorities account results in delicate programs, their presence raises severe flags. “Uncovered authorities credentials could possibly be doubtlessly used for focused spear-phishing, impersonation, or as an entry level into authorities networks,” Fowler famous.
How the info was seemingly collected
So, the place did this mountain of information come from?
The proof factors to “infostealer” malware. This can be a sort of malicious software program that, as soon as put in on a sufferer’s system, silently information each keystroke, together with usernames and passwords, and sends it again to a hacker’s server.
The database’s technical setup was basic for this type of operation. It was designed to routinely index and arrange a continuing stream of stolen information for straightforward looking. Disturbingly, Fowler reported that the variety of information elevated throughout the practically month-long means of getting it taken down, which means new sufferer information was pouring in whilst he tried to sound the alarm.
“The database appeared to retailer keylogging and ‘infostealer’ malware,” Fowler said. The construction allowed anybody with an online browser to go looking by the hundreds of thousands of compromised accounts.
A irritating rakedown and lasting threat
Discovering the database proprietor proved not possible as a result of it had no figuring out info. Fowler needed to report it on to the internet hosting supplier. He described a sluggish, complicated course of involving a world host and an unbiased subsidiary earlier than the info was lastly secured.
The large drawback? The horse has already bolted. Whereas this particular open server is now closed, the 149 million credentials are virtually actually already within the arms of criminals. They’ll use them for “credential stuffing” assaults (making an attempt the identical password on different websites), id theft, monetary fraud, or extremely convincing phishing schemes.
What you are able to do now
This incident is a brutal reminder that credential theft is an industrialized enterprise. As Fowler put it, this discovery “highlights the worldwide risk posed by credential-stealing malware.”
Right here’s find out how to defend your self:
- Assume you could be affected. With numbers this massive, it’s a secure wager.
- Change your passwords, beginning with e mail and monetary accounts. By no means reuse passwords throughout completely different websites.
- Allow two-factor authentication (2FA) in every single place it’s supplied. This provides a essential second step for logging in.
- Use a respected antivirus software program to scan your units. If a tool is contaminated with an infostealer, merely altering passwords received’t assist, because the malware will simply steal the brand new ones.
- Be additional vigilant for phishing emails, particularly ones that appear to learn about your accounts or on-line habits.
Associated studying: Google can be tightening entry controls throughout its ecosystem. Right here’s why Gmail is ending Gmailify and POP3 help, and what it means for account safety.



