“Vibe coding” — utilizing AI fashions to assist write code — has turn out to be a part of on a regular basis growth for lots of groups. It may be an enormous time-saver, however it will probably additionally result in over-trusting AI-generated code, which creates room for safety vulnerabilities to be launched.
Intruder’s expertise serves as a real-world case research in how AI-generated code can influence safety. Right here’s what occurred and what different organizations ought to look ahead to.
When We Let AI Assist Construct a Honeypot
To ship our Fast Response service, we arrange honeypots designed to gather early-stage exploitation makes an attempt. For certainly one of them, we couldn’t discover an open-source possibility that did precisely what we needed, so we did what loads of groups do nowadays: we used AI to assist draft a proof-of-concept.
It was deployed as deliberately weak infrastructure in an remoted atmosphere, however we nonetheless gave the code a fast sanity examine earlier than rolling it out.
Just a few weeks later, one thing odd began exhibiting up within the logs. Recordsdata that ought to have been saved underneath attacker IP addresses had been showing with payload strings as a substitute, which made it clear that person enter was ending up someplace we didn’t intend.

The Vulnerability We Didn’t See Coming
A more in-depth inspection of the code confirmed what was occurring: the AI had added logic to drag client-supplied IP headers and deal with them because the customer’s IP.
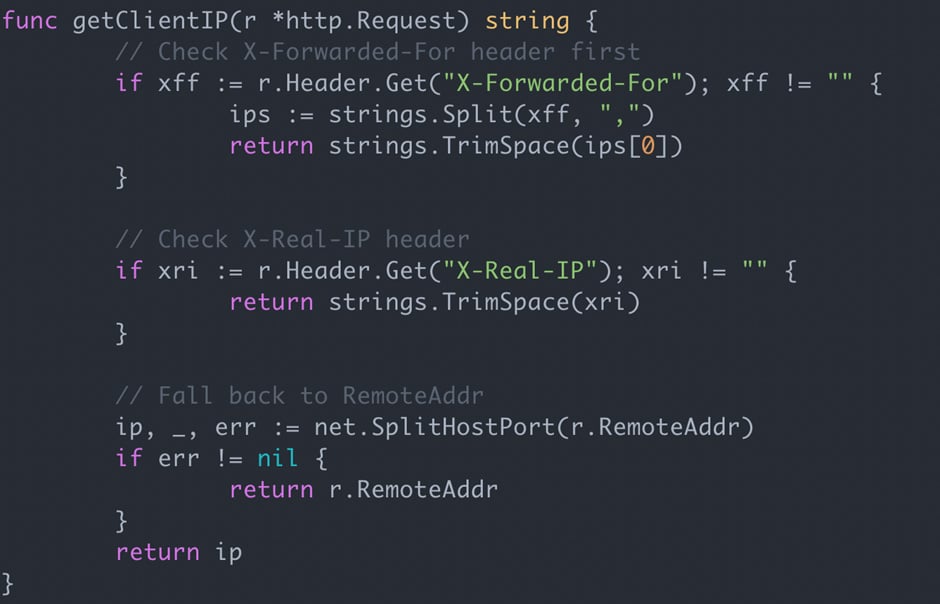
This could solely be protected if the headers come from a proxy you management; in any other case they’re successfully underneath the shopper’s management.
This implies the location customer can simply spoof their IP handle or use the header to inject payloads, which is a vulnerability we regularly discover in penetration assessments.
In our case, the attacker had merely positioned their payload into the header, which defined the bizarre listing names. The influence right here was low and there was no signal of a full exploit chain, but it surely did give the attacker some affect over how this system behaved.
It may have been a lot worse: if we had been utilizing the IP handle in one other method, the identical mistake may have simply led to Native File Disclosure or Server-Aspect Request Forgery.
The menace atmosphere is intensifying and attackers are shifting quicker with AI.
Constructed on insights from 3,000+ organizations, Intruder’s Publicity Administration Index reveals how defenders are adapting. Get the complete evaluation and benchmark your staff’s time-to-fix.
Why SAST Missed It
We ran Semgrep OSS and Gosec on the code. Neither flagged the vulnerability, though Semgrep did report just a few unrelated enhancements. That’s not a failure of these instruments — it’s a limitation of static evaluation.
Detecting this specific flaw requires contextual understanding that the client-supplied IP headers had been getting used with out validation, and that no belief boundary was enforced.
It’s the form of nuance that’s apparent to a human pentester, however simply missed when reviewers place somewhat an excessive amount of confidence in AI-generated code.
AI Automation Complacency
There’s a well-documented concept from aviation that supervising automation takes extra cognitive effort than performing the duty manually. The identical impact appeared to point out up right here.
As a result of the code wasn’t ours within the strict sense — we didn’t write the traces ourselves — the psychological mannequin of the way it labored wasn’t as robust, and overview suffered.
The comparability to aviation ends there, although. Autopilot programs have many years of security engineering behind them, whereas AI-generated code doesn’t. There isn’t but a longtime security margin to fall again on.
This Wasn’t an Remoted Case
This wasn’t the one case the place AI confidently produced insecure outcomes. We used the Gemini reasoning mannequin to assist generate customized IAM roles for AWS, which turned out to be weak to privilege escalation. Even after we identified the difficulty, the mannequin politely agreed after which produced one other weak function.
It took 4 rounds of iteration to reach at a protected configuration. At no level did the mannequin independently acknowledge the safety downside – it required human steering your entire approach.
Skilled engineers will often catch these points. However AI-assisted growth instruments are making it simpler for individuals with out safety backgrounds to supply code, and latest analysis has already discovered hundreds of vulnerabilities launched by such platforms.
However as we’ve proven, even skilled builders and safety professionals can overlook flaws when the code comes from an AI mannequin that appears assured and behaves accurately at first look. And for end-users, there’s no approach to inform whether or not the software program they depend on accommodates AI-generated code, which places the duty firmly on the organizations delivery the code.
Takeaways for Groups Utilizing AI
At a minimal, we don’t advocate letting non-developers or non-security employees depend on AI to write down code.
And in case your group does permit consultants to make use of these instruments, it’s price revisiting your code overview course of and CI/CD detection capabilities to ensure this new class of points doesn’t slip by means of.
We anticipate AI-introduced vulnerabilities to turn out to be extra widespread over time.
Few organizations will overtly admit when a problem got here from their use of AI, so the dimensions of the issue might be bigger than what’s reported. This received’t be the final instance — and we doubt it’s an remoted one.
Ebook a demo to see how Intruder uncovers exposures earlier than they turn out to be breaches.
Creator
Sam Pizzey is a Safety Engineer at Intruder. Beforehand a pentester somewhat too obsessive about reverse engineering, at present targeted on methods to detect software vulnerabilities remotely at scale.
Sponsored and written by Intruder.


