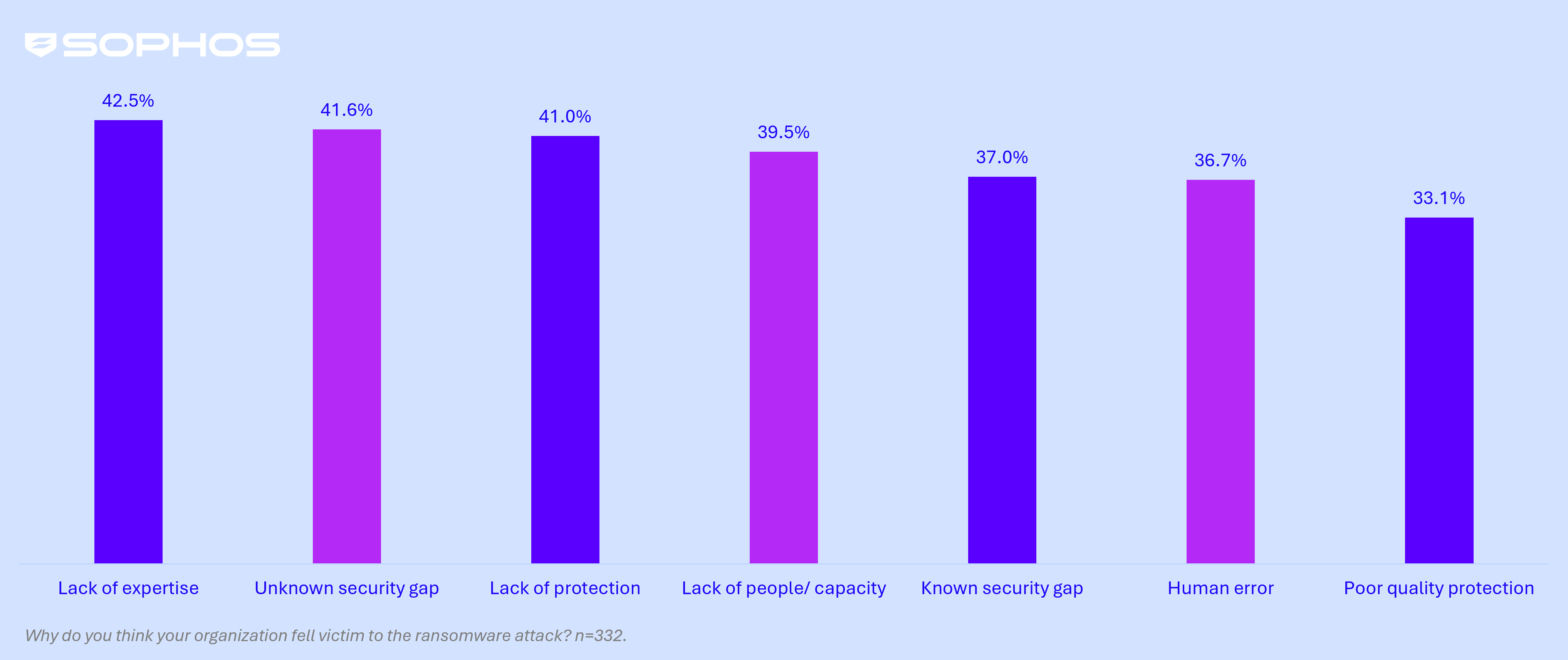Sophos’ newest annual research explores the real-world ransomware experiences of 332 manufacturing and manufacturing organizations hit by ransomware up to now 12 months. The report examines how the causes and penalties of those assaults have developed over time.
This 12 months’s version additionally sheds new mild on beforehand unexplored areas, together with the organizational elements that left companies uncovered and the human toll ransomware takes on IT and cybersecurity groups throughout the sector.
Obtain the report back to discover the complete findings.
Exploited vulnerabilities and experience shortfalls gas ransomware incidents
Exploited vulnerabilities are the main root explanation for ransomware assaults on manufacturing and manufacturing organizations, accountable for 32% of incidents. Malicious emails ranked second, with their share declining from 29% in 2024 to 23% in 2025.
A number of organizational elements contribute to manufacturing and manufacturing organizations falling sufferer to ransomware, with the most typical being a lack of information (i.e., inadequate abilities or data obtainable to detect and cease the assault in time) named by 42.5% of victims. It’s adopted in very shut succession by unknown safety gaps (i.e., weaknesses in defenses that respondents have been unaware of), which contributed to 41.6% of assaults.
Organizational root explanation for assaults in manufacturing and manufacturing
Knowledge encryption sharply declines however extortion charges soar
Knowledge encryption within the sector has dropped to its lowest stage in 5 years, with 40% of assaults leading to information being encrypted — the third lowest share recorded on this 12 months’s survey and near half the 74% reported by manufacturing and manufacturing organizations in 2024. In keeping with this pattern, the share of assaults stopped earlier than encryption reached a five-year excessive, indicating that manufacturing and manufacturing organizations are strengthening their defenses.
Nonetheless, adversaries are adapting: The proportion of producing and manufacturing organizations hit by extortion-only assaults (the place information wasn’t encrypted however a ransom was nonetheless demanded) surged to 10% of assaults in 2025 from simply 3% in 2024 — the second highest price reported on this 12 months’s survey. That is seemingly as a result of excessive worth of mental property, advanced provide chains, and the operational affect of downtime in manufacturing environments.
Knowledge encryption in manufacturing and manufacturing | 2021 – 2025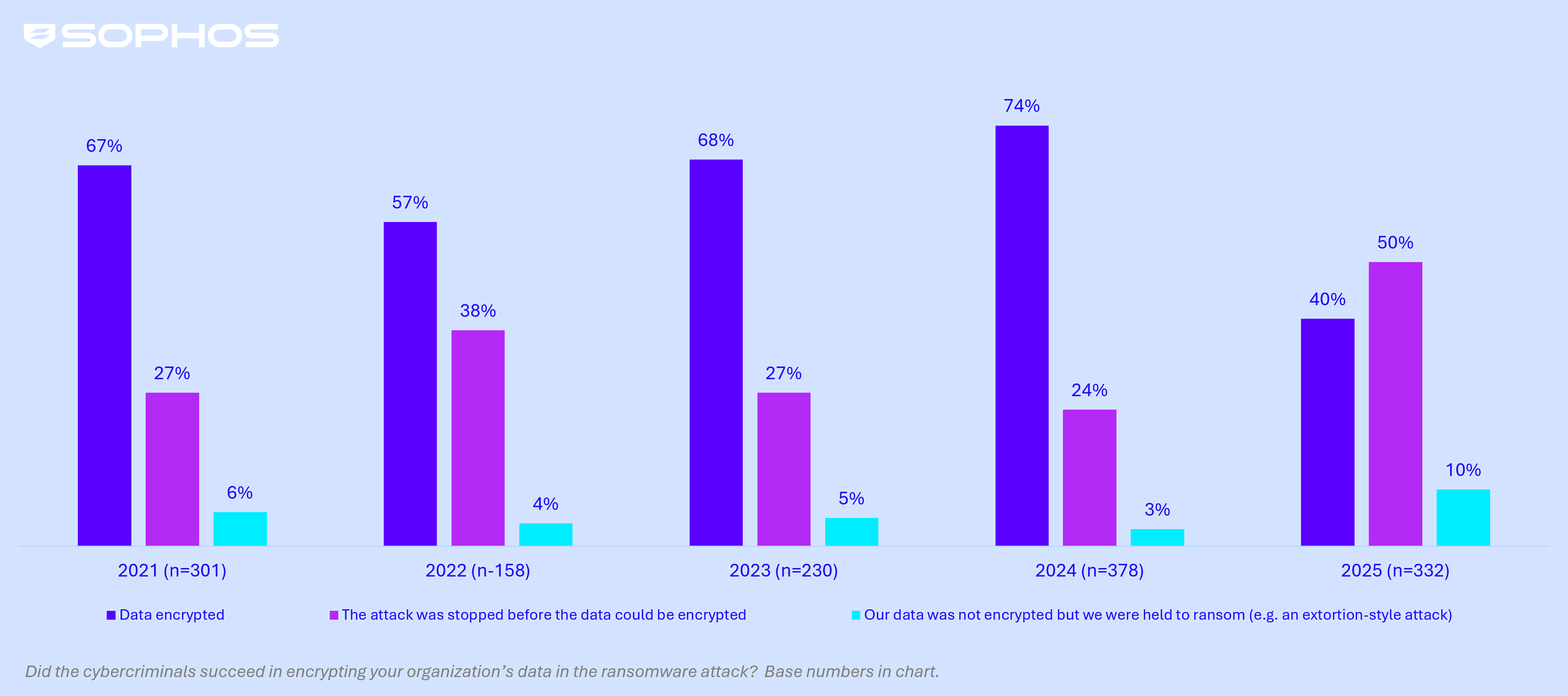
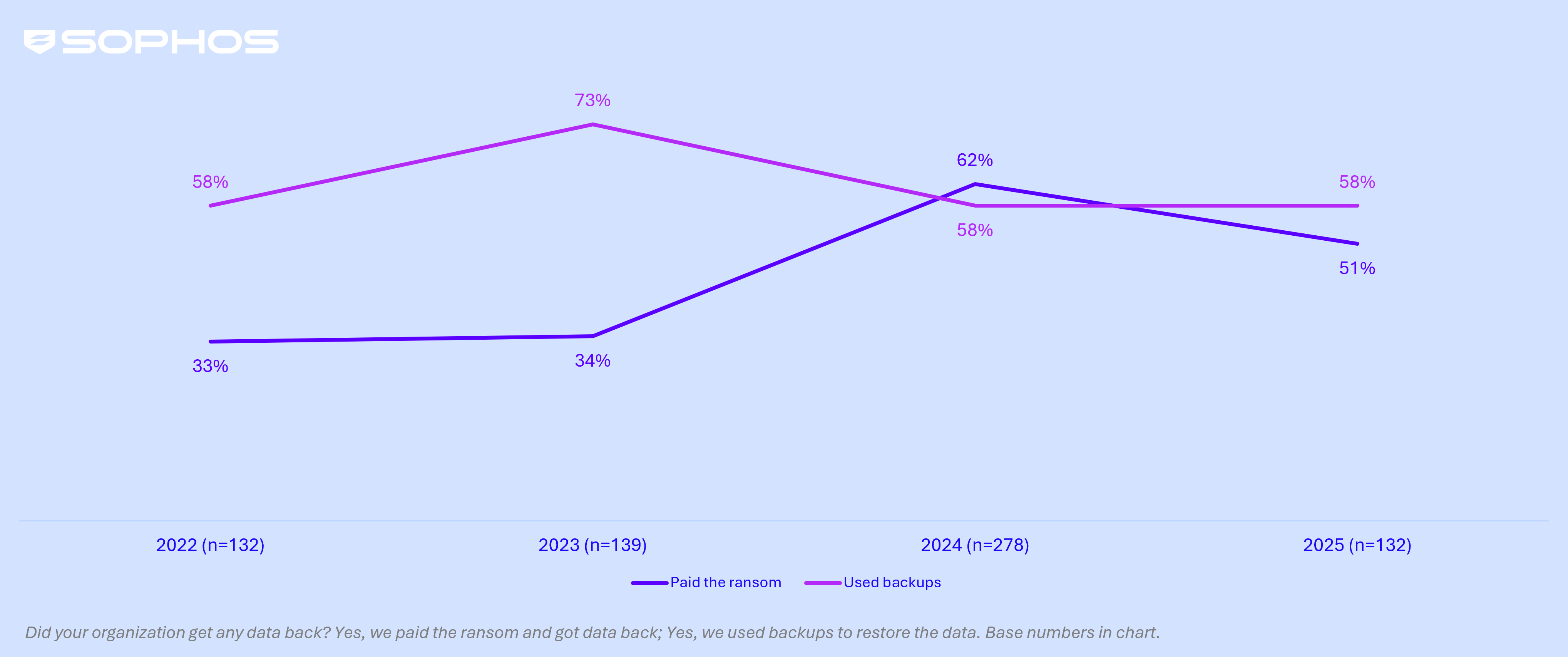
Ransom funds persist whereas reliance on backups maintain regular
Whereas the proportion of producing and manufacturing organizations paying the ransom to get better information has declined within the final 12 months, over half (51%) nonetheless paid — effectively above 2022 (33%) and 2023 (34%) ranges. In the meantime, backup use stays regular at 58% in 2025, reflecting sturdy confidence on this information restoration methodology.
Restoration of encrypted information in manufacturing and manufacturing | 2021 – 2025
Ransom calls for, funds and assault restoration prices fall
Ransomware economics in manufacturing and manufacturing shifted in 2025, with common ransom calls for falling 20% to $1.2M (from $1.5M in 2024) and funds dropping from $1.2M to $1.0M. The decline was largely pushed by fewer mid-range ($1M–$5M) calls for and payouts, whereas excessive circumstances ($5M+) noticed a slight uptick.
On the similar time, the imply price of restoration (excluding any ransoms paid) has dropped practically 1 / 4 (24%) over the previous 12 months to $1.3M, down from $1.7M in 2024 and under the $1.5M world common on this 12 months’s report.
Collectively, these findings point out that the sector is changing into extra resilient and environment friendly in its ransomware response however nonetheless faces high-value outliers that skew the general threat panorama.
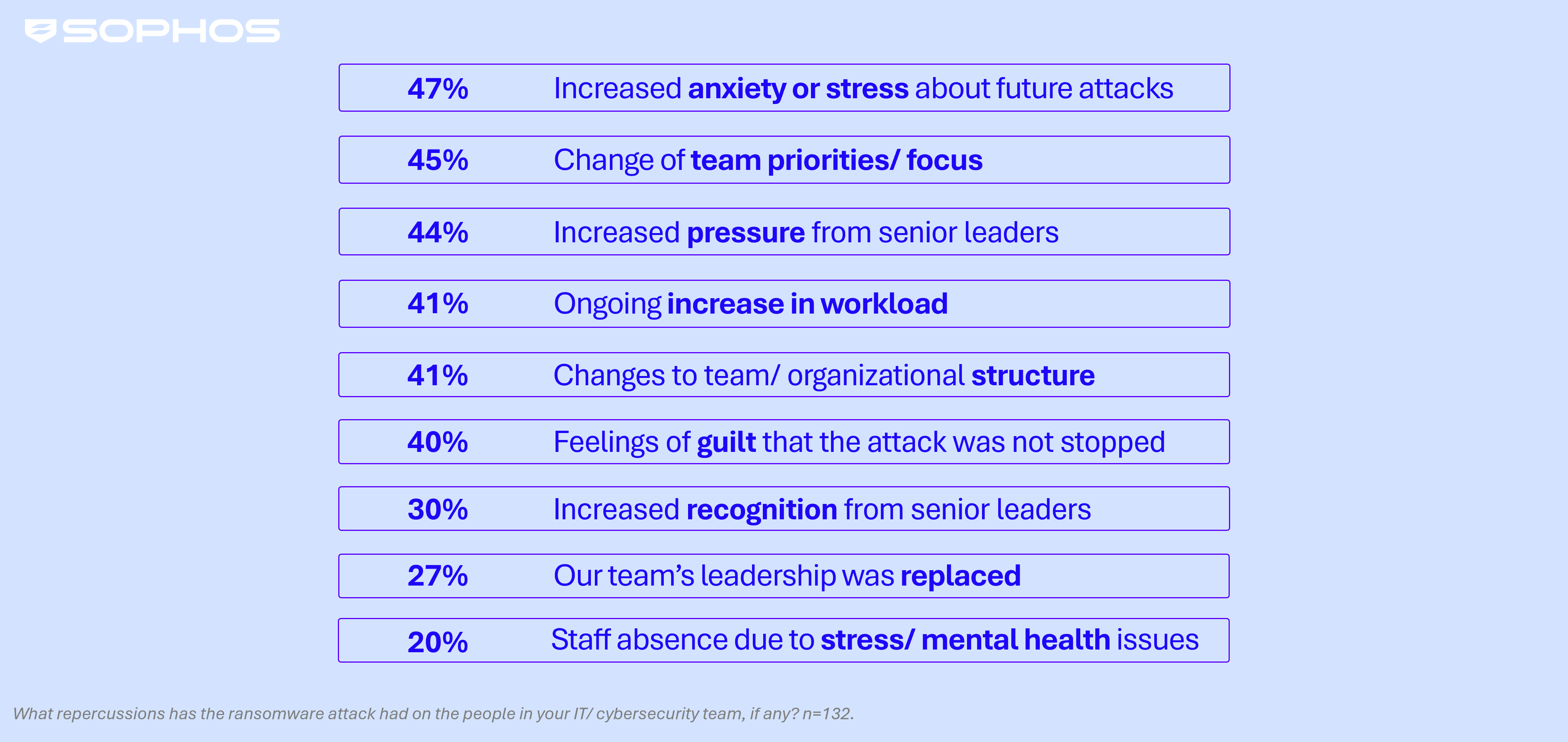
Ransomware takes a human toll, driving stress and nervousness amongst IT/cybersecurity groups throughout the sector
The survey reveals that ransomware incidents have profound repercussions for IT and cybersecurity groups within the manufacturing and manufacturing sector. Practically half of respondents (47%) reported elevated nervousness or stress about future assaults, underscoring the lasting psychological affect of such occasions.
Different widespread penalties embrace a shift in crew priorities or focus (45%), heightened strain from senior management (44%), and a sustained improve in workload (41%). Notably, the proportion of producing and manufacturing respondents reporting these results was greater than the cross-sector common throughout practically all areas, highlighting the distinctive pressure confronted by groups on this trade.
Obtain the complete report for extra insights into the human and monetary impacts of ransomware on the retail sector.
What Sophos is seeing within the manufacturing sector
Along with the findings of the report, over the previous twelve months, Sophos X-Ops has noticed ransomware exercise throughout leak websites and located that 99 distinct risk teams focused manufacturing organizations. Probably the most distinguished teams focusing on manufacturing organizations based mostly on leak web site observations are GOLD SAHARA (Akira), GOLD FEATHER (Qilin) and GOLD ENCORE (PLAY). Reflecting the tendencies within the report, over half of the ransomware incidents dealt with by Sophos Emergency Incident Response concerned each information theft and information encryption, underscoring the continued rise of double extortion techniques the place stolen information is held to ransom and threatened with publication on a leak web site.
In regards to the survey
The report relies on the findings of an unbiased, vendor-agnostic survey commissioned by Sophos of three,400 IT/cybersecurity leaders throughout 17 nations within the Americas, EMEA, and Asia Pacific, together with 332 from the manufacturing and manufacturing sector. All respondents signify organizations with between 100 and 5,000 workers. The survey was carried out by analysis specialist Vanson Bourne between January and March 2025, and members have been requested to reply based mostly on their experiences over the earlier 12 months.