The second Shai-Hulud assault final week uncovered round 400,000 uncooked secrets and techniques after infecting lots of of packages within the NPM (Node Package deal Supervisor) registry and publishing stolen knowledge in 30,000 GitHub repositories.
Though nearly 10,000 of the uncovered secrets and techniques have been verified as legitimate by the open-source TruffleHog scanning instrument, researchers at cloud safety platform Wiz say that greater than 60% of the leaked NPM tokens have been nonetheless legitimate as of December 1st.
The Shai-Hulud menace emerged in mid-September, compromising 187 NPM packages with a self-propagating payload that recognized account tokens utilizing TruffleHog, injected a malicious script into the packages, and routinely revealed them on the platform.
Within the second assault, the malware impacted over 800 packages (counting all contaminated variations of a bundle) and included a harmful mechanism that wiped the sufferer’s house listing if sure situations have been met.
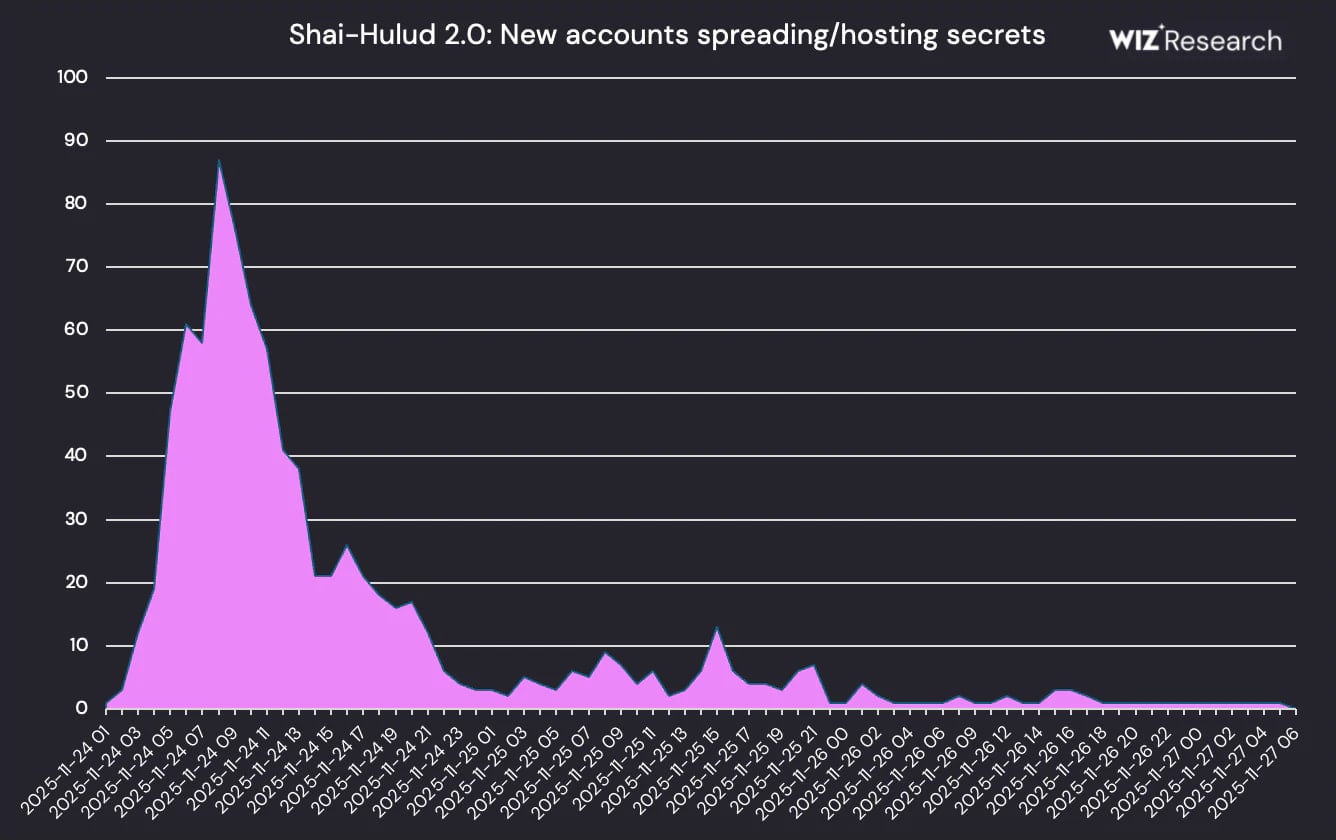
Supply: Wiz
Wiz researchers analyzing the leak of secrets and techniques that the Shai-Hulud 2.0 assault unfold over 30,000 GitHub repositories, discovered that the next forms of secrets and techniques have been uncovered:
- about 70% of the repositories had a contents.json file with GitHub usernames and tokens, and file snapshots
- half of them had the truffleSecrets.json file containing TruffleHog scan outcomes
- 80% of the repositories had the surroundings.json file with OS data, CI/CD metadata, npm bundle metadata, and GitHub credentials
- 400 repositories hosted the actionsSecrets.json with GitHub Actions workflow secrets and techniques
Wiz notes that the malware used TruffleHog with out the ‘-only-verified’ flag, which means that the 400,000 uncovered secrets and techniques match a recognized format and might not be legitimate or usable anymore.
“Whereas the key knowledge is extraordinarily noisy and requires heavy deduplication efforts, it nonetheless accommodates lots of of legitimate secrets and techniques, together with cloud, NPM tokens, and VCS credentials,” defined Wiz.
“To this point, these credentials pose an lively danger of additional provide chain assaults. For instance, we observe that over 60% of leaked NPM tokens are nonetheless legitimate.”
Evaluation of 24,000 surroundings.json information confirmed that roughly half of them have been distinctive, with 23% akin to developer machines, and the remaining coming from CI/CD runners and comparable infrastructure.
The info compiled by the researchers reveals that a lot of the contaminated machines, 87% of them, are Linux methods, whereas most infections (76%) have been on containers.
Concerning the CI/CD platform distribution, GitHub Actions led by far, adopted by Jenkins, GitLab CI, and AWS CodeBuild.
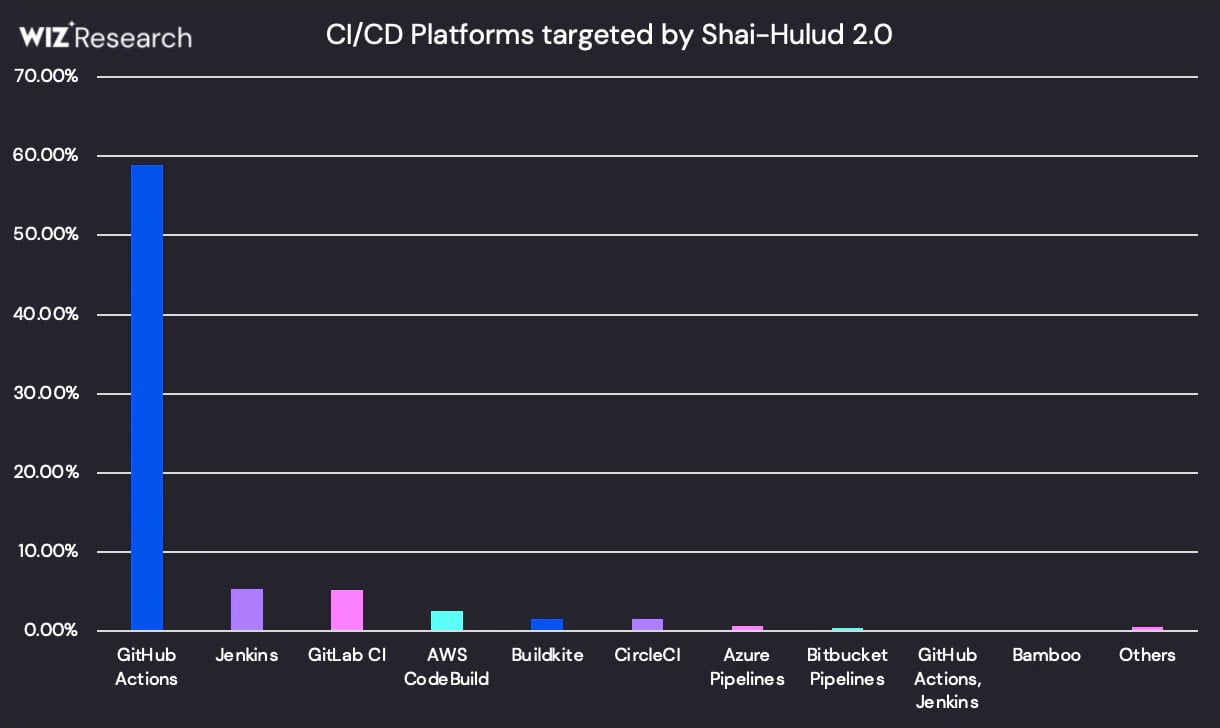
Supply: Wiz
Trying on the an infection distribution, Wiz researchers discovered that the highest bundle was @postman/tunnel-agent@0.6.7, adopted by @asyncapi/specs@6.8.3. These two packages collectively accounted for greater than 60% of all of the infections.
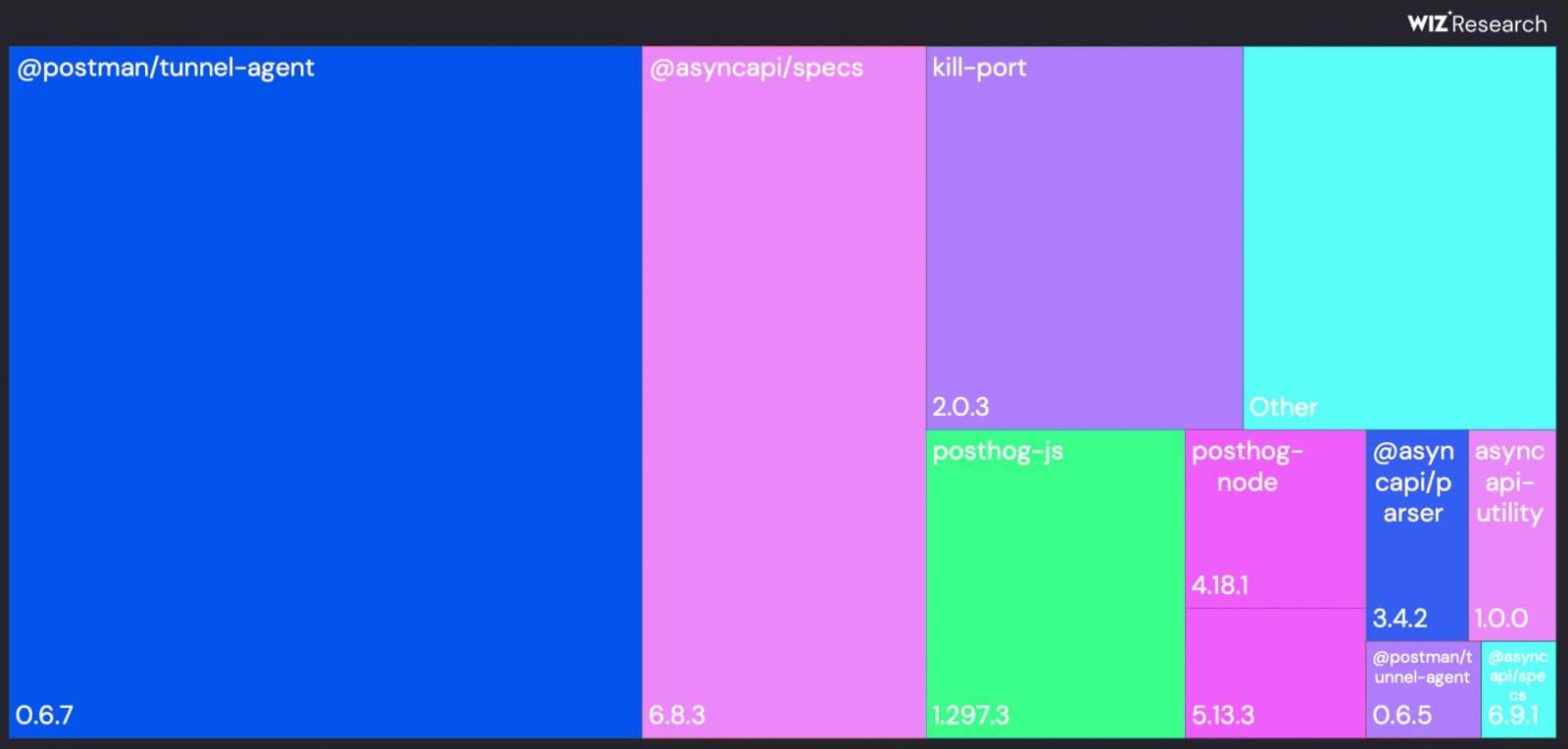
Supply: Wiz
Due to this focus, the researchers say that the Shai-Hulud influence may have been vastly diminished if a couple of key packages had been recognized and neutralized early on.
Equally, in regards to the an infection sample, 99% of situations got here from the preinstall occasion operating node setup_bun.js, and the only a few exceptions have been doubtless testing makes an attempt.
Wiz believes that the perpetrators behind Shai-Hulud will proceed to refine and evolve their methods, and predicts that extra assault waves will emerge within the close to future, probably leveraging the huge credential trove harvested up to now.
Damaged IAM is not simply an IT drawback – the influence ripples throughout your entire enterprise.
This sensible information covers why conventional IAM practices fail to maintain up with trendy calls for, examples of what “good” IAM appears to be like like, and a easy guidelines for constructing a scalable technique.



